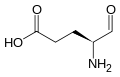
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | {{Short description|Overview of Glutamate-1-semialdehyde}} | ||
{{Chembox | |||
| Name = Glutamate-1-semialdehyde | |||
| ImageFile = <!-- Image file name --> | |||
| ImageSize = 200px | |||
| IUPACName = 2-Amino-5-oxopentanoic acid | |||
| OtherNames = Glutamate semialdehyde | |||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| CASNo = 35376-70-0 | |||
| PubChem = 439409 | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 388454 | |||
}} | |||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | |||
| Formula = C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>9</sub>NO<sub>3</sub> | |||
| MolarMass = 131.13 g/mol | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
'''Glutamate-1-semialdehyde''' is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of [[porphyrins]] and [[chlorophyll]]. It is a derivative of [[glutamic acid]] and plays a crucial role in the [[C5 pathway]] of [[tetrapyrrole]] synthesis. | |||
[[ | == Biosynthesis == | ||
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde is synthesized from [[glutamyl-tRNA]] by the enzyme [[glutamyl-tRNA reductase]]. This reaction is a key step in the conversion of [[glutamate]] to [[5-aminolevulinic acid]] (ALA), which is the first common precursor in the biosynthesis of all tetrapyrroles, including [[heme]], [[chlorophyll]], and [[vitamin B12]]. | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
In the [[C5 pathway]], glutamate-1-semialdehyde is converted to [[5-aminolevulinic acid]] by the enzyme [[glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase]]. This conversion is essential for the production of [[porphyrin]] rings, which are the building blocks of many important biological molecules. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | |||
Disruptions in the biosynthesis of glutamate-1-semialdehyde can lead to disorders in [[heme]] production, such as [[porphyria]]. Understanding the role of glutamate-1-semialdehyde in these pathways can help in the development of treatments for such conditions. | |||
== | == See also == | ||
* [[Porphyrin synthesis]] | |||
* [[Chlorophyll biosynthesis]] | |||
* [[Tetrapyrrole]] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
== | |||
[[Category:Biochemistry]] | [[Category:Biochemistry]] | ||
[[Category:Metabolism]] | [[Category:Metabolism]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glutamate-1-semialdehyde.svg|Glutamate-1-semialdehyde | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:21, 3 March 2025
Overview of Glutamate-1-semialdehyde
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of porphyrins and chlorophyll. It is a derivative of glutamic acid and plays a crucial role in the C5 pathway of tetrapyrrole synthesis.
Biosynthesis[edit]
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde is synthesized from glutamyl-tRNA by the enzyme glutamyl-tRNA reductase. This reaction is a key step in the conversion of glutamate to 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), which is the first common precursor in the biosynthesis of all tetrapyrroles, including heme, chlorophyll, and vitamin B12.
Function[edit]
In the C5 pathway, glutamate-1-semialdehyde is converted to 5-aminolevulinic acid by the enzyme glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. This conversion is essential for the production of porphyrin rings, which are the building blocks of many important biological molecules.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Disruptions in the biosynthesis of glutamate-1-semialdehyde can lead to disorders in heme production, such as porphyria. Understanding the role of glutamate-1-semialdehyde in these pathways can help in the development of treatments for such conditions.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
Glutamate-1-semialdehyde