Energy crop: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Biofuel-stub}} | {{Biofuel-stub}} | ||
{{Biomass-stub}} | {{Biomass-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:DEFRA_Energy_Crops_scheme_plantation_-_geograph.org.uk_-_848101.jpg|Energy crop plantation | |||
File:Public_Footpath_Through_Elephant_Grass_-_geograph.org.uk_-_291522.jpg|Public footpath through elephant grass | |||
File:Kerala_coconut.jpg|Coconut plantation in Kerala | |||
File:Bequer-B100-SOJA-SOYBEAM.jpg|Soybean field | |||
File:Panicum_virgaturn_heavy_metal_switch_grass_MN_2007.JPG|Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) | |||
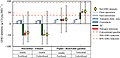
File:GHG_(CO2_and_N2O)_life_cycle_emissions_for_Miscanthus_x_giganteus_and_SRC_Poplar.jpg|GHG life cycle emissions for Miscanthus and SRC Poplar | |||
File:Miscanthus_Bestand.JPG|Miscanthus field | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:13, 18 February 2025
Energy crops are plant species cultivated specifically for their ability to produce energy, usually in the form of biofuel or biomass. These crops are a key component of sustainable energy solutions and are an alternative to fossil fuels.
Overview[edit]
Energy crops are typically high-yield plants which are harvested to produce bioenergy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuel. They are a type of biomass, organic material that can be used as a renewable energy source. Energy crops can be categorized into two main types: herbaceous and woody crops.
Types of Energy Crops[edit]
Herbaceous Crops[edit]
Herbaceous energy crops are non-woody plants that are harvested annually. Examples include corn, sugarcane, and switchgrass. These crops are often used to produce ethanol, a type of biofuel.
Woody Crops[edit]
Woody energy crops are tree species that are harvested every few years. Examples include poplar trees and willow trees. These crops are often used to produce biodiesel or to generate heat and electricity.
Benefits and Challenges[edit]
Energy crops offer several benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving energy security, and providing opportunities for rural development. However, they also present challenges, such as potential competition with food crops for land and water resources, and the need for significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
See Also[edit]
-
Energy crop plantation
-
Public footpath through elephant grass
-
Coconut plantation in Kerala
-
Soybean field
-
Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum)
-
GHG life cycle emissions for Miscanthus and SRC Poplar
-
Miscanthus field