Hydroponics: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Soilless culture]] | [[Category:Soilless culture]] | ||
{{horticulture-stub}} | {{horticulture-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Hydroponic_onions,_NASA_--_17_June_2004.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Hydro_system.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:CDC_South_Aquaponics_Raft_Tank_1_2010-07-17.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Leafy_Greens_Hydroponics.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Systeme_AEROPONIC_573px.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Water-cultivate_a_crocus.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Systeme_FLOOD&DRAIN_573px.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Bengal_System.png|Hydroponics | |||
File:Expo_2015_-_Coltura_idroponica_al_padiglione_del_Belgio.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Rockwool_4lbs_per_ft3_fibrex5.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Hydroton.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
File:Mother_plants_in_flower.jpg|Hydroponics | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:51, 18 February 2025
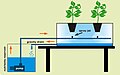
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture, which is a method of growing plants without soil, by instead using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent.
History[edit]
The concept of hydroponics dates back to the ancient civilizations of Egypt and Babylon, with the Hanging Gardens of Babylon often considered one of the earliest examples of hydroponics. Modern hydroponics was introduced in the 1920s as a means of commercial plant production.
Types of Hydroponics[edit]
There are several types of hydroponics systems, including the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Aeroponics.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a hydroponic technique wherein a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients required for plant growth is recirculated past the bare roots of plants in a watertight gully.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) is a hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water.
- Aeroponics is the process of growing plants in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
Hydroponics has several advantages over soil cultivation. The growth rate of a hydroponic plant is 30-50 percent faster than a soil plant. However, hydroponics also has its disadvantages, such as the potential for water-based diseases and the high cost of setup.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This article is a horticulture stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics
-
Hydroponics