GABAB receptor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{GPCR-stub}} | {{GPCR-stub}} | ||
{{neuroscience-stub}} | {{neuroscience-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:6VJM_GABAB_Receptor_dimer_inactive.png|Inactive GABAB Receptor Dimer | |||
File:Gamma-Aminobuttersäure_-_gamma-aminobutyric_acid.svg|Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) | |||
File:4-Hydroxybutansäure_-_4-Hydroxybutanoic_acid.svg|4-Hydroxybutanoic Acid | |||
File:Lesogaberan.svg|Lesogaberan | |||
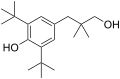
File:CGP-7930_chemical_structure.svg|CGP-7930 Chemical Structure | |||
File:Phaclofen.svg|Phaclofen | |||
File:SCH-50911.svg|SCH-50911 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:15, 18 February 2025
GABAB receptor
The GABAB receptor is a type of G protein-coupled receptor that is activated by the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is found in the central nervous system and plays a crucial role in inhibitory neurotransmission.
Structure[edit]
The GABAB receptor is a heterodimer, composed of two subunits, GABAB1 and GABAB2. Each subunit has a seven-transmembrane domain, similar to other G protein-coupled receptors. The GABAB1 subunit is responsible for ligand-binding, while the GABAB2 subunit is involved in the activation of the G protein.
Function[edit]
Upon activation by GABA, the GABAB receptor inhibits the activity of adenylyl cyclase, reducing the production of cyclic AMP. This leads to a decrease in the activity of protein kinase A, resulting in hyperpolarization of the neuron and inhibition of neurotransmission.
The GABAB receptor also plays a role in the regulation of synaptic plasticity, and is involved in the modulation of long-term potentiation and depression.
Clinical significance[edit]
Alterations in GABAB receptor function have been implicated in a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including epilepsy, schizophrenia, depression, and addiction.
GABAB receptor agonists, such as baclofen, are used clinically for the treatment of spasticity and certain types of neuropathic pain. Antagonists of the GABAB receptor, such as phaclofen and saclofen, are used in research to study the receptor's function.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
This GPCR-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Inactive GABAB Receptor Dimer
-
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
-
4-Hydroxybutanoic Acid
-
Lesogaberan
-
CGP-7930 Chemical Structure
-
Phaclofen
-
SCH-50911