Transesophageal echocardiogram: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Transesophageal Echocardiogram == | |||
A '''transesophageal echocardiogram''' (TEE) is a type of [[echocardiography]] that provides detailed images of the heart and its structures. Unlike a standard [[transthoracic echocardiogram]], TEE involves inserting a specialized probe into the [[esophagus]], which is located close to the heart, allowing for clearer and more precise images. | |||
== Procedure == | |||
The | The TEE procedure begins with the patient being sedated to ensure comfort. A flexible probe with an ultrasound transducer at its tip is then gently guided down the throat into the esophagus. This position allows the transducer to capture high-resolution images of the heart without interference from the [[ribs]] or [[lungs]]. | ||
== | === Indications === | ||
TEE is particularly useful in diagnosing and evaluating conditions such as: | |||
* [[Endocarditis]] | |||
* [[Congenital heart defects]] | |||
* [[Aortic dissection]] | |||
* [[Valvular heart disease]] | |||
* [[Cardiac masses]] | |||
== | === Advantages === | ||
The proximity of the esophagus to the heart allows TEE to provide superior image quality compared to transthoracic echocardiography. This makes it invaluable in situations where detailed visualization of the heart's structures is necessary. | |||
== | == Images == | ||
[[File:TEE-Sonde.png|thumb|right|Diagram of a TEE probe.]] | |||
[[File:Transesophageal_echocardiography_diagram.svg|thumb|right|Illustration showing the position of the TEE probe.]] | |||
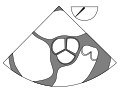
* [[ | [[File:ME_four_chamber_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|thumb|right|Mid-esophageal four-chamber view.]] | ||
* [[ | [[File:ME_AV_SAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|thumb|right|Mid-esophageal aortic valve short-axis view.]] | ||
* [[ | [[File:ME_two-chamber_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|thumb|right|Mid-esophageal two-chamber view.]] | ||
[[File:ME_AV_LAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|thumb|right|Mid-esophageal aortic valve long-axis view.]] | |||
[[File:UE_aortic_arch_LAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|thumb|right|Upper esophageal aortic arch long-axis view.]] | |||
== Risks and Complications == | |||
While TEE is generally safe, it does carry some risks, including: | |||
* Sore throat | |||
* Esophageal perforation | |||
* Bleeding | |||
* Reaction to sedation | |||
Patients are monitored closely during and after the procedure to manage any potential complications. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Echocardiography]] | |||
* [[Cardiac imaging]] | |||
* [[Heart disease]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Cardiac imaging]] | |||
[[Category:Medical tests]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:TEE-Sonde.png|Transesophageal echocardiogram probe | |||
File:Transesophageal_echocardiography_diagram.svg|Diagram of transesophageal echocardiography | |||
File:ME_four_chamber_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|Mid-esophageal four chamber view | |||
File:ME_AV_SAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|Mid-esophageal aortic valve short axis view | |||
File:ME_two-chamber_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|Mid-esophageal two chamber view | |||
File:ME_AV_LAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|Mid-esophageal aortic valve long axis view | |||
File:UE_aortic_arch_LAX_(CardioNetworks_ECHOpedia).svg|Upper esophageal aortic arch long axis view | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:21, 18 February 2025
Transesophageal Echocardiogram[edit]
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is a type of echocardiography that provides detailed images of the heart and its structures. Unlike a standard transthoracic echocardiogram, TEE involves inserting a specialized probe into the esophagus, which is located close to the heart, allowing for clearer and more precise images.
Procedure[edit]
The TEE procedure begins with the patient being sedated to ensure comfort. A flexible probe with an ultrasound transducer at its tip is then gently guided down the throat into the esophagus. This position allows the transducer to capture high-resolution images of the heart without interference from the ribs or lungs.
Indications[edit]
TEE is particularly useful in diagnosing and evaluating conditions such as:
Advantages[edit]
The proximity of the esophagus to the heart allows TEE to provide superior image quality compared to transthoracic echocardiography. This makes it invaluable in situations where detailed visualization of the heart's structures is necessary.
Images[edit]







Risks and Complications[edit]
While TEE is generally safe, it does carry some risks, including:
- Sore throat
- Esophageal perforation
- Bleeding
- Reaction to sedation
Patients are monitored closely during and after the procedure to manage any potential complications.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Transesophageal echocardiogram probe
-
Diagram of transesophageal echocardiography
-
Mid-esophageal four chamber view
-
Mid-esophageal aortic valve short axis view
-
Mid-esophageal two chamber view
-
Mid-esophageal aortic valve long axis view
-
Upper esophageal aortic arch long axis view