Rhomboid fossa: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Rhomboid fossa == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray649.png|Rhomboid fossa | |||
File:Gray709.png|Rhomboid fossa | |||
File:Gray719.png|Rhomboid fossa | |||
File:Gray785.png|Rhomboid fossa | |||
File:Human caudal brainstem posterior view description.JPG|Rhomboid fossa | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:43, 20 February 2025
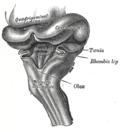
Rhomboid fossa is a part of the human brain, specifically located in the fourth ventricle. It is a diamond-shaped depression and plays a crucial role in the functioning of the nervous system.
Anatomy[edit]
The Rhomboid fossa is located in the dorsal part of the fourth ventricle, between the cerebellum and the dorsal surface of the pons and medulla oblongata. It is named for its rhomboid or diamond shape.
Function[edit]
The Rhomboid fossa is involved in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It contains several openings, including the median aperture and the two lateral apertures, which allow CSF to exit the ventricle and enter the subarachnoid space.
Clinical significance[edit]
Abnormalities or damage to the Rhomboid fossa can lead to a variety of neurological disorders, including hydrocephalus, a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of CSF in the brain.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />