Otoplasty: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Johann_Friedrich_Dieffenbach.jpg|Otoplasty | |||
File:Earcov.JPG|Otoplasty | |||
File:Otopexy_prae.jpg|Otoplasty | |||
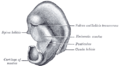
File:Gray904.png|Otoplasty | |||
File:Processusmastoideusossistemporalis.PNG|Otoplasty | |||
File:Auricularis_posterior.png|Otoplasty | |||
File:Gray905.png|Otoplasty | |||
File:Gray906.png|Otoplasty | |||
File:Darwin-s-tubercle.jpg|Otoplasty | |||
File:Microtia_lvl3.jpg|Otoplasty | |||
File:Dr._Placik_Chicago_Plastic_Surgeon_Earwell_19828.jpg|Otoplasty | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:42, 18 February 2025
Otoplasty is a type of cosmetic surgery that is performed to change the shape, position, or size of the ears. It can also be used to correct defects that are present from birth, or those that have been caused by injury.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure for otoplasty varies depending on the specific needs of the patient. However, it generally involves making a small incision behind the ear to expose the cartilage. The surgeon then reshapes the cartilage and secures it in its new position with stitches. In some cases, excess skin may also be removed.
Recovery[edit]
Following the procedure, patients may experience some discomfort and swelling, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days. A bandage is typically worn around the head for a week to protect the ears and help them heal in their new position.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any surgical procedure, otoplasty carries some risks. These may include infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. There is also the possibility that the patient may not be satisfied with the results of the surgery.