North America: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==North America== | |||
[[File:Location_North_America.svg|thumb|right|Map showing the location of North America.]] | |||
'''North America''' is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. It covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), about 16.5% of the Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. | |||
North America | |||
== | ==Geography== | ||
[[File:Map_of_populous_North_America_(physical,_political,_population).jpg|thumb|left|Physical, political, and population map of North America.]] | |||
North America | |||
North America is the third largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. The continent is divided into three large countries: [[Canada]], the [[United States]], and [[Mexico]], along with the smaller countries of [[Central America]] and the [[Caribbean]]. | |||
== | The continent's geography is diverse, ranging from the Arctic tundra of northern Canada and Alaska to the tropical rainforests of Central America. The [[Rocky Mountains]] and the [[Appalachian Mountains]] are two major mountain ranges, while the [[Great Plains]] and the [[Mississippi River]] basin are significant geographical features. | ||
==History== | |||
* [[ | [[File:Historisch_Nordamerika_(cropped).jpg|thumb|right|Historical map of North America.]] | ||
The history of North America is rich and varied, with indigenous peoples inhabiting the continent for thousands of years before the arrival of European explorers. The [[Vikings]] were among the first Europeans to reach North America, landing in what is now Newfoundland, Canada, around the year 1000. | |||
In 1492, [[Christopher Columbus]] reached the Caribbean, marking the beginning of sustained European contact with the Americas. This led to the colonization of the continent by European powers, including Spain, France, and England. The subsequent centuries saw the establishment of European colonies, the displacement and decline of indigenous populations, and the eventual emergence of independent nations. | |||
==Economy== | |||
North America has a diverse and highly developed economy. The United States and Canada are among the world's largest economies, with significant industrial and technological sectors. Mexico is a major emerging market, with a growing manufacturing base and a significant oil industry. | |||
The continent is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, and fossil fuels. Agriculture is also a key sector, with the United States and Canada being major producers of wheat, corn, and other crops. | |||
==Culture== | |||
North America is culturally diverse, with a rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, European influences, and more recent immigrant communities. The continent is home to a wide variety of languages, religions, and cultural practices. | |||
The United States is known for its cultural exports, including music, film, and technology, which have a global influence. Canada is recognized for its multiculturalism and bilingualism, while Mexico is celebrated for its rich cultural heritage, including its cuisine, art, and festivals. | |||
==Environment== | |||
[[File:North_America_satellite_orthographic.jpg|thumb|left|Satellite image of North America.]] | |||
North America's environment is diverse, with a wide range of ecosystems and climates. The continent is home to vast forests, expansive deserts, and extensive coastlines. Environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution are significant challenges facing the continent. | |||
Conservation efforts are underway to protect North America's natural heritage, including national parks, wildlife reserves, and international agreements aimed at preserving biodiversity and reducing environmental impact. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Canada]] | |||
* [[United States]] | |||
* [[Mexico]] | |||
* [[Central America]] | |||
* [[Caribbean]] | |||
[[Category:North America]] | [[Category:North America]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:21, 23 March 2025
North America[edit]

North America is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. It covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), about 16.5% of the Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface.
Geography[edit]

North America is the third largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. The continent is divided into three large countries: Canada, the United States, and Mexico, along with the smaller countries of Central America and the Caribbean.
The continent's geography is diverse, ranging from the Arctic tundra of northern Canada and Alaska to the tropical rainforests of Central America. The Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains are two major mountain ranges, while the Great Plains and the Mississippi River basin are significant geographical features.
History[edit]

The history of North America is rich and varied, with indigenous peoples inhabiting the continent for thousands of years before the arrival of European explorers. The Vikings were among the first Europeans to reach North America, landing in what is now Newfoundland, Canada, around the year 1000.
In 1492, Christopher Columbus reached the Caribbean, marking the beginning of sustained European contact with the Americas. This led to the colonization of the continent by European powers, including Spain, France, and England. The subsequent centuries saw the establishment of European colonies, the displacement and decline of indigenous populations, and the eventual emergence of independent nations.
Economy[edit]
North America has a diverse and highly developed economy. The United States and Canada are among the world's largest economies, with significant industrial and technological sectors. Mexico is a major emerging market, with a growing manufacturing base and a significant oil industry.
The continent is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, and fossil fuels. Agriculture is also a key sector, with the United States and Canada being major producers of wheat, corn, and other crops.
Culture[edit]
North America is culturally diverse, with a rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, European influences, and more recent immigrant communities. The continent is home to a wide variety of languages, religions, and cultural practices.
The United States is known for its cultural exports, including music, film, and technology, which have a global influence. Canada is recognized for its multiculturalism and bilingualism, while Mexico is celebrated for its rich cultural heritage, including its cuisine, art, and festivals.
Environment[edit]
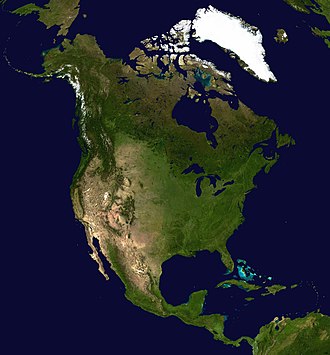
North America's environment is diverse, with a wide range of ecosystems and climates. The continent is home to vast forests, expansive deserts, and extensive coastlines. Environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and pollution are significant challenges facing the continent.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect North America's natural heritage, including national parks, wildlife reserves, and international agreements aimed at preserving biodiversity and reducing environmental impact.