Pollen: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Pollen == | |||
== Structure | [[File:Misc_pollen_colorized.jpg|thumb|right|Colorized scanning electron micrograph of pollen grains from a variety of common plants: sunflower (Helianthus annuus), morning glory (Ipomoea purpurea), prairie hollyhock (Sidalcea malviflora), oriental lily (Lilium auratum), evening primrose (Oenothera fruticosa), and castor bean (Ricinus communis).]] | ||
Pollen grains | |||
'''Pollen''' is a fine to coarse powdery substance comprising [[pollen grain]]s, which are male microgametophytes of seed plants, responsible for the production of male gametes (sperm cells). Each pollen grain contains a vegetative (non-reproductive) cell, and a generative (reproductive) cell that divides to form two sperm cells. | |||
== Structure == | |||
[[File:Oenothera_speciosa_pollen_200x.jpg|thumb|left|Pollen of ''Oenothera speciosa'' at 200x magnification.]] | |||
Pollen grains have a hard coat made of [[sporopollenin]] that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of coniferous plants. The structure of pollen grains varies among species, which can be used to identify the plant species from which they originate. | |||
== Function == | |||
The primary function of pollen is to transfer male genetic material from one plant to another, facilitating [[fertilization]] and the production of seeds. Pollen is produced in the [[anther]]s of the [[stamen]]s in [[angiosperms]] and in the [[microsporangium]] of [[gymnosperms]]. | |||
== Pollen Tube == | |||
[[File:Pollen_Tube.svg|thumb|right|Diagram of a pollen tube growing through the style to reach the ovule.]] | |||
Once a pollen grain lands on a compatible [[stigma]], it germinates and grows a pollen tube down the style to the ovule. The sperm cells travel through this tube to reach the egg cell, resulting in fertilization. | |||
== Types of Pollen == | == Types of Pollen == | ||
[[File:Lilium_auratum_-_pollen.jpg|thumb|left|Pollen of ''Lilium auratum'' (golden-rayed lily).]] | |||
Pollen | Pollen can be classified based on its source plant. For example, pollen from [[angiosperms]] is often sticky and heavy, adapted for transport by animals, while pollen from [[gymnosperms]] is typically lighter and adapted for wind dispersal. | ||
== | == Pollen Viability == | ||
== | [[File:Жизнеспособность_пыльцы_13.jpg|thumb|right|Testing pollen viability.]] | ||
* [[ | Pollen viability refers to the ability of pollen to germinate and effect fertilization. Factors affecting viability include environmental conditions, storage, and the age of the pollen. | ||
* [[ | |||
* [[ | == Pollen and Pollination == | ||
* [[ | |||
[[File:Fire_lily_pollens_on_an_insect's_hair.jpg|thumb|left|Pollen grains on an insect's hair, demonstrating the role of insects in pollination.]] | |||
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male part of a plant to the female part, enabling fertilization. This can occur via wind, water, or animals, with insects being the most common pollinators. | |||
== Pollen Development == | |||
[[File:Coenocytic_Tetrad.gif|thumb|right|Animation of pollen development showing a coenocytic tetrad.]] | |||
Pollen development begins with the formation of microspores in the [[anther]]s. These microspores undergo mitosis to form pollen grains, which are released when the anther dehisces. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Pollination]] | |||
* [[Anther]] | |||
* [[Stamen]] | |||
* [[Fertilization (biology)]] | |||
* [[Sporopollenin]] | |||
[[Category:Plant anatomy]] | [[Category:Plant anatomy]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Pollination]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:15, 21 February 2025
Pollen[edit]
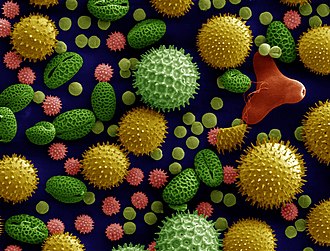
Pollen is a fine to coarse powdery substance comprising pollen grains, which are male microgametophytes of seed plants, responsible for the production of male gametes (sperm cells). Each pollen grain contains a vegetative (non-reproductive) cell, and a generative (reproductive) cell that divides to form two sperm cells.
Structure[edit]

Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of coniferous plants. The structure of pollen grains varies among species, which can be used to identify the plant species from which they originate.
Function[edit]
The primary function of pollen is to transfer male genetic material from one plant to another, facilitating fertilization and the production of seeds. Pollen is produced in the anthers of the stamens in angiosperms and in the microsporangium of gymnosperms.
Pollen Tube[edit]

Once a pollen grain lands on a compatible stigma, it germinates and grows a pollen tube down the style to the ovule. The sperm cells travel through this tube to reach the egg cell, resulting in fertilization.
Types of Pollen[edit]

Pollen can be classified based on its source plant. For example, pollen from angiosperms is often sticky and heavy, adapted for transport by animals, while pollen from gymnosperms is typically lighter and adapted for wind dispersal.
Pollen Viability[edit]

Pollen viability refers to the ability of pollen to germinate and effect fertilization. Factors affecting viability include environmental conditions, storage, and the age of the pollen.
Pollen and Pollination[edit]

Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male part of a plant to the female part, enabling fertilization. This can occur via wind, water, or animals, with insects being the most common pollinators.
Pollen Development[edit]

Pollen development begins with the formation of microspores in the anthers. These microspores undergo mitosis to form pollen grains, which are released when the anther dehisces.