Nanotechnology: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
== Nanotechnology == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Fullerene_Nanogears_-_GPN-2000-001535.jpg|Fullerene Nanogears | |||
File:Comparison_of_nanomaterials_sizes.jpg|Comparison of Nanomaterials Sizes | |||
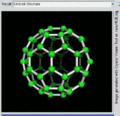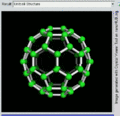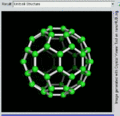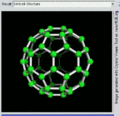
File:C60_Molecule.svg|C60 Molecule | |||
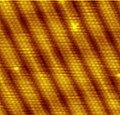
File:Atomic_resolution_Au100.JPG|Atomic Resolution Au100 | |||
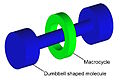
File:Rotaxane_cartoon.jpg|Rotaxane Cartoon | |||
File:DNA_tetrahedron_white.png|DNA Tetrahedron | |||
File:C60_Buckyball.gif|C60 Buckyball | |||
File:Achermann7RED.jpg|Achermann7RED | |||
File:AFMsetup.jpg|AFM Setup | |||
File:Threshold_formation_nowatermark.gif|Threshold Formation | |||
File:A-simple-and-fast-fabrication-of-a-both-self-cleanable-and-deep-UV-antireflective-quartz-1556-276X-7-430-S1.ogv|A Simple and Fast Fabrication of a Both Self-Cleanable and Deep UV Antireflective Quartz | |||
File:Nanowire_laser.png|Nanowire Laser | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:26, 23 February 2025
Nanotechnology is a field of research and innovation concerned with building 'things' - generally, materials and devices - on the scale of atoms and molecules. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter. A sheet of paper is about 100,000 nanometers thick; a single gold atom is about a third of a nanometer in diameter. Instances of nanoscale structures include tuberculosis, a carbon nanotube, and DNA.
History[edit]
The concept of nanotechnology was introduced by Richard Feynman in his talk There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom, in which he described the possibility of synthesis via direct manipulation of atoms. The term "nano-technology" was first used by Norio Taniguchi in 1974.
Fundamental concepts[edit]
Nanotechnology is science, engineering, and technology conducted at the nanoscale, which is about 1 to 100 nanometers. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology.
Applications[edit]
Nanotechnology may be able to create many new materials and devices with a vast range of applications, such as in nanomedicine, nanoelectronics, biomaterials energy production, and consumer products.
Implications[edit]
Nanotechnology raises many of the same issues as any new technology, including concerns about the toxicity and environmental impact of nanomaterials, and their potential effects on global economics, as well as speculation about various doomsday scenarios.
See also[edit]
- List of nanotechnology applications
- Nanotechnology in fiction
- Nanomedicine
- Nanoelectronics
- Nanomaterials
- Molecular nanotechnology
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
|
|
|
Nanotechnology[edit]
-
Fullerene Nanogears
-
Comparison of Nanomaterials Sizes
-
C60 Molecule
-
Atomic Resolution Au100
-
Rotaxane Cartoon
-
DNA Tetrahedron
-
C60 Buckyball
-
Achermann7RED
-
AFM Setup
-
Threshold Formation
-
A Simple and Fast Fabrication of a Both Self-Cleanable and Deep UV Antireflective Quartz
-
Nanowire Laser