Meristem: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
== Meristem == | |||
<gallery> | |||
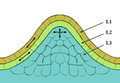
File:Méristème_couches.png|Meristem layers | |||
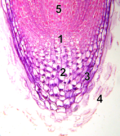
File:Méristème_coupe_zones_chiffres.png|Meristem section with numbered zones | |||
File:Apical_Meristems_in_Crassula_ovata.png|Apical Meristems in Crassula ovata | |||
File:Root-tip-tag.png|Root tip | |||
File:Linaria_spur.jpg|Linaria spur | |||
File:Cardamine_hirsuta.jpg|Cardamine hirsuta | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:11, 23 February 2025
Meristem
The Meristem is a type of tissue found in plants that is responsible for growth. It is composed of undifferentiated cells, which have the ability to divide and differentiate into various types of cells and tissues. This process is known as cellular differentiation.
Types of Meristem[edit]
There are three types of meristem, namely the apical meristem, the lateral meristem, and the intercalary meristem.
Apical Meristem[edit]
The apical meristem is located at the tips of roots and shoots and is responsible for the vertical growth of the plant. It gives rise to three types of primary meristems, which are the protoderm, the procambium, and the ground meristem.
Lateral Meristem[edit]
The lateral meristem is responsible for the horizontal growth of the plant. It is found in the stems and roots and gives rise to two types of secondary meristems, which are the vascular cambium and the cork cambium.
Intercalary Meristem[edit]
The intercalary meristem is found at the base of the leaves or internodes. It is responsible for the elongation of the plant parts and helps in the regeneration of cut parts.
Function of Meristem[edit]
The primary function of the meristem is to facilitate growth. The cells in the meristem are capable of continuous division, which allows for the addition of new cells and tissues. This process is crucial for the growth and development of the plant.