Electric potential: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:VFPt_metal_balls_largesmall_potential+contour.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:VFPt_plus_thumb_potential+contour.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:VFPt_minus_thumb_potential+contour.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:VFPt_charges_plus_minus_potential+contour.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Electric_potential_varying_charge.gif|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_infinite_wire_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_infinite_plane_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_infinite_cylinder_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_solid_sphere_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_spherical_surface_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_ring_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
File:Charged_disc_problem.svg|Electric potential | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:14, 18 February 2025
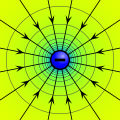
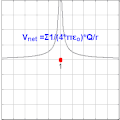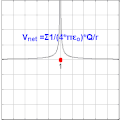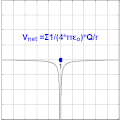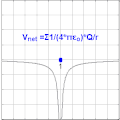
Electric potential is a fundamental concept in physics and electromagnetism, defined as the amount of electric potential energy that a charged particle would have if located at a specific point in space. It is also known as the electric potential difference and is measured in volts.
Definition[edit]
The electric potential at a point in space is defined as the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit positive charge from a reference point to that point without any acceleration. It is important to note that the reference point is usually taken at infinity.
Mathematical Representation[edit]
The electric potential V at a point r in a static electric field E is given by the line integral:
- V = - ∫ E • dl
where dl is an infinitesimal element of the path.
Relation with Electric Field[edit]
The electric potential is related to the electric field by the equation:
- E = - ∇V
where ∇V is the gradient of the electric potential.
Applications[edit]
Electric potential has numerous applications in various fields such as electronics, electrical engineering, and physics. It is used in the design of electric circuits, capacitors, and batteries. It also plays a crucial role in understanding phenomena like electric discharge, electric shock, and electric current.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />