Patellar dislocation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Patellar dislocation | |||
| image = [[File:PetellardislocationChildMark.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = Patellar dislocation in a child | |||
| field = [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Knee pain]], [[swelling]], [[instability]] | |||
| complications = [[Recurrent dislocation]], [[osteoarthritis]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, often during [[sports]] or [[trauma]] | |||
| duration = Varies, can be acute or chronic | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[congenital]] factors, [[ligament laxity]] | |||
| risks = [[Adolescence]], [[female gender]], [[sports participation]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Knee sprain]], [[meniscus tear]], [[ACL injury]] | |||
| prevention = [[Strengthening exercises]], [[knee braces]] | |||
| treatment = [[Reduction (orthopedic)]], [[physical therapy]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment, risk of recurrence | |||
| frequency = Common in adolescents and young adults | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Knee_diagram.svg|left|thumb|Diagram of the knee]] | |||
[[File:Patellaluxation_ap_001.png|left|thumb|Patellar dislocation (AP view)]] | |||
[[File:Lateral_patellofemoral_angle.jpg|left|thumb|Lateral patellofemoral angle]] | |||
[[File:Lateral_and_medial_joint_space_of_patella.jpg|left|thumb|Lateral and medial joint space of patella]] | |||
[[File:Patella_Luxation_coronar3.png|thumb|Patella luxation (coronal view)]] | |||
'''Patellar Dislocation''' is a medical condition where the [[patella]] or kneecap moves out of its normal location. It often occurs as a result of a sudden change in direction when the leg is planted on the ground. The patella moves out of the groove and stays to the outside of the knee. | '''Patellar Dislocation''' is a medical condition where the [[patella]] or kneecap moves out of its normal location. It often occurs as a result of a sudden change in direction when the leg is planted on the ground. The patella moves out of the groove and stays to the outside of the knee. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Patellar dislocation can occur due to a variety of reasons. It can be caused by a direct blow or sudden twist of the knee, or it can occur due to weak muscles and ligaments that support the knee joint. Other factors that can contribute to patellar dislocation include [[hypermobile joints]], flat feet, and a high-riding patella. | Patellar dislocation can occur due to a variety of reasons. It can be caused by a direct blow or sudden twist of the knee, or it can occur due to weak muscles and ligaments that support the knee joint. Other factors that can contribute to patellar dislocation include [[hypermobile joints]], flat feet, and a high-riding patella. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The most common symptoms of a patellar dislocation include pain and swelling in the knee, inability to straighten the knee, feeling of the knee giving way, and visible deformity, with the kneecap being out of place. | The most common symptoms of a patellar dislocation include pain and swelling in the knee, inability to straighten the knee, feeling of the knee giving way, and visible deformity, with the kneecap being out of place. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of patellar dislocation is usually made based on a physical examination and medical history. Imaging tests such as [[X-ray]]s, [[MRI]]s, or [[CT scan]]s may be used to confirm the diagnosis and to check for any associated injuries such as bone fractures or damage to the ligaments. | The diagnosis of patellar dislocation is usually made based on a physical examination and medical history. Imaging tests such as [[X-ray]]s, [[MRI]]s, or [[CT scan]]s may be used to confirm the diagnosis and to check for any associated injuries such as bone fractures or damage to the ligaments. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment for patellar dislocation depends on the severity of the dislocation and the patient's overall health. Initial treatment often involves reducing the dislocation, which is the process of putting the kneecap back into place. This is usually followed by immobilization of the knee using a knee brace or cast. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve its stability. In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair damaged structures or realign the knee joint. | The treatment for patellar dislocation depends on the severity of the dislocation and the patient's overall health. Initial treatment often involves reducing the dislocation, which is the process of putting the kneecap back into place. This is usually followed by immobilization of the knee using a knee brace or cast. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve its stability. In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair damaged structures or realign the knee joint. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Prevention of patellar dislocation involves strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of dislocation. | Prevention of patellar dislocation involves strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of dislocation. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Knee pain]] | * [[Knee pain]] | ||
* [[Knee injuries]] | * [[Knee injuries]] | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] | * [[Physical therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic disorders]] | [[Category:Orthopedic disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Injuries]] | [[Category:Injuries]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 00:56, 14 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Patellar dislocation | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Knee pain, swelling, instability |
| Complications | Recurrent dislocation, osteoarthritis |
| Onset | Sudden, often during sports or trauma |
| Duration | Varies, can be acute or chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, congenital factors, ligament laxity |
| Risks | Adolescence, female gender, sports participation |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Knee sprain, meniscus tear, ACL injury |
| Prevention | Strengthening exercises, knee braces |
| Treatment | Reduction (orthopedic), physical therapy, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment, risk of recurrence |
| Frequency | Common in adolescents and young adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
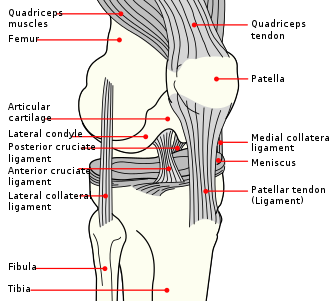




Patellar Dislocation is a medical condition where the patella or kneecap moves out of its normal location. It often occurs as a result of a sudden change in direction when the leg is planted on the ground. The patella moves out of the groove and stays to the outside of the knee.
Causes[edit]
Patellar dislocation can occur due to a variety of reasons. It can be caused by a direct blow or sudden twist of the knee, or it can occur due to weak muscles and ligaments that support the knee joint. Other factors that can contribute to patellar dislocation include hypermobile joints, flat feet, and a high-riding patella.
Symptoms[edit]
The most common symptoms of a patellar dislocation include pain and swelling in the knee, inability to straighten the knee, feeling of the knee giving way, and visible deformity, with the kneecap being out of place.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of patellar dislocation is usually made based on a physical examination and medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be used to confirm the diagnosis and to check for any associated injuries such as bone fractures or damage to the ligaments.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for patellar dislocation depends on the severity of the dislocation and the patient's overall health. Initial treatment often involves reducing the dislocation, which is the process of putting the kneecap back into place. This is usually followed by immobilization of the knee using a knee brace or cast. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve its stability. In severe cases, surgery may be required to repair damaged structures or realign the knee joint.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of patellar dislocation involves strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of dislocation.


