Kallikrein: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Kallikrein''' is a | '''Kallikrein''' is a subgroup of serine proteases that are involved in various physiological processes, including blood coagulation, inflammation, and [[fibrinolysis]]. These enzymes are known for their ability to cleave peptide bonds in proteins, thereby activating or inactivating them. | ||
== Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
Kallikreins are characterized by their serine protease activity, which means they have a serine residue at their active site that plays a crucial role in their enzymatic function. They are synthesized as inactive precursors called zymogens and are activated by proteolytic cleavage. | |||
Kallikreins are involved in | Kallikreins are involved in the [[kinin-kallikrein system]], where they cleave kininogen to release [[bradykinin]], a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate and lowers blood pressure. This system plays a significant role in the regulation of blood pressure, inflammation, and pain. | ||
Kallikreins | == Types of Kallikreins == | ||
There are two main types of kallikreins: | |||
* '''Plasma kallikrein''': This type circulates in the blood and is involved in the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. It also plays a role in the activation of the complement system. | |||
* '''Tissue kallikrein''': Found in various tissues, this type is involved in the local generation of kinins and other biologically active peptides. | |||
== Role in Fibrinolysis == | |||
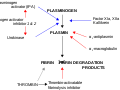
Kallikrein plays a crucial role in the process of fibrinolysis, which is the breakdown of fibrin in blood clots. It activates plasminogen to plasmin, the enzyme responsible for degrading fibrin. This process is essential for maintaining blood flow and preventing thrombosis. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | |||
Dysregulation of kallikrein activity can lead to various medical conditions. For example, excessive kallikrein activity can result in hereditary angioedema, a condition characterized by episodes of severe swelling. Conversely, insufficient kallikrein activity can contribute to hypertension and thrombosis. | |||
Kallikreins are also being studied as potential biomarkers for certain cancers, such as prostate cancer, where kallikrein-related peptidase 3 (KLK3), also known as [[prostate-specific antigen]] (PSA), is used in screening and monitoring. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Serine protease]] | |||
* [[Kinin-kallikrein system]] | * [[Kinin-kallikrein system]] | ||
* [[Fibrinolysis]] | |||
* [[Bradykinin]] | * [[Bradykinin]] | ||
* [[Prostate-specific antigen]] | |||
* [[Prostate | |||
[[Category:Proteases]] | |||
[[Category:Enzymes]] | [[Category:Enzymes]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Fibrinolysis.svg|Kallikrein | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:05, 20 February 2025
Kallikrein is a subgroup of serine proteases that are involved in various physiological processes, including blood coagulation, inflammation, and fibrinolysis. These enzymes are known for their ability to cleave peptide bonds in proteins, thereby activating or inactivating them.
Structure and Function[edit]
Kallikreins are characterized by their serine protease activity, which means they have a serine residue at their active site that plays a crucial role in their enzymatic function. They are synthesized as inactive precursors called zymogens and are activated by proteolytic cleavage.
Kallikreins are involved in the kinin-kallikrein system, where they cleave kininogen to release bradykinin, a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate and lowers blood pressure. This system plays a significant role in the regulation of blood pressure, inflammation, and pain.
Types of Kallikreins[edit]
There are two main types of kallikreins:
- Plasma kallikrein: This type circulates in the blood and is involved in the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. It also plays a role in the activation of the complement system.
- Tissue kallikrein: Found in various tissues, this type is involved in the local generation of kinins and other biologically active peptides.
Role in Fibrinolysis[edit]
Kallikrein plays a crucial role in the process of fibrinolysis, which is the breakdown of fibrin in blood clots. It activates plasminogen to plasmin, the enzyme responsible for degrading fibrin. This process is essential for maintaining blood flow and preventing thrombosis.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Dysregulation of kallikrein activity can lead to various medical conditions. For example, excessive kallikrein activity can result in hereditary angioedema, a condition characterized by episodes of severe swelling. Conversely, insufficient kallikrein activity can contribute to hypertension and thrombosis.
Kallikreins are also being studied as potential biomarkers for certain cancers, such as prostate cancer, where kallikrein-related peptidase 3 (KLK3), also known as prostate-specific antigen (PSA), is used in screening and monitoring.
Related Pages[edit]
-
Kallikrein