Buccal administration: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Buccal_Mucosa.png | |||
File:Zoobies.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:10, 17 February 2025
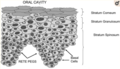
Buccal administration is a topical route of pharmaceutical drug administration. This method involves placing a drug between the gums and the cheek, where it dissolves and is absorbed into the bloodstream. This method is considered a good alternative to oral administration, especially for patients who have difficulty swallowing.
Overview[edit]
Buccal administration is a form of administration that involves delivering a substance via the buccal mucosa (the lining of the cheek and the area between the gums and upper and lower lips). The drug is typically placed in the mouth, against the cheek, and allowed to dissolve. This method of administration is often used for drugs that are intended to act locally in the mouth, such as local anesthetics.
Advantages[edit]
Buccal administration has several advantages over other forms of drug administration. It allows for a rapid onset of action, as the drug is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. It also avoids the first-pass metabolism, which can lead to a reduction in the effectiveness of some drugs. Additionally, buccal administration can be more comfortable and convenient for patients, particularly those who have difficulty swallowing.
Disadvantages[edit]
Despite its advantages, buccal administration also has some disadvantages. The drug must be able to dissolve in the saliva in order to be absorbed, which limits the types of drugs that can be administered this way. Additionally, the drug may not be fully absorbed if the patient swallows before the drug has fully dissolved. Finally, some patients may find the taste of the drug unpleasant.
Drugs commonly administered buccally[edit]
Several types of drugs are commonly administered buccally. These include analgesics, antiemetics, antidepressants, antipsychotics, cardiovascular drugs, hormones, and sedatives.