Medulloblastoma: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Medulloblastoma | |||
| image = [[File:CT_brain_scan_of_child_with_medulloblastoma_and_resulting_hydrocephalus.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = CT brain scan of a child with medulloblastoma and resulting hydrocephalus | |||
| field = [[Neuro-oncology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Headache]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[ataxia]], [[dizziness]], [[vision problems]] | |||
| complications = [[Hydrocephalus]], [[cerebellar mutism syndrome]] | |||
| onset = Most common in children | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| types = Classic, Desmoplastic/nodular, Large cell/anaplastic, Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Genetic syndromes]] (e.g., [[Gorlin syndrome]], [[Turcot syndrome]]) | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Ependymoma]], [[astrocytoma]], [[brainstem glioma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[radiation therapy]], [[chemotherapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on age, tumor subtype, and extent of disease | |||
| frequency = Most common malignant brain tumor in children | |||
}} | |||
== Medulloblastoma: An Introduction == | == Medulloblastoma: An Introduction == | ||
'''Medulloblastoma''' is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern. | '''Medulloblastoma''' is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern. | ||
[[File:AFIP405851R-MEDULLOBLASTOMA.jpg|left|thumb|250px|MRI scan showing a medulloblastoma.]] | |||
[[File:AFIP405851R-MEDULLOBLASTOMA.jpg|thumb | |||
== Anatomy and Localization == | == Anatomy and Localization == | ||
Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions. | Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/sIJAwE0enpo | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/sIJAwE0enpo | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 19: | Line 33: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Cerebellum: The Origin Site == | == Cerebellum: The Origin Site == | ||
* The [[cerebellum]] is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination. | |||
* The [[cerebellum]] is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination. | |||
* Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms. | * Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth. | Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth. | ||
* '''Balance and Coordination Issues:''' Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements. | * '''Balance and Coordination Issues:''' Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements. | ||
* '''Headaches and Nausea:''' Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea. | * '''Headaches and Nausea:''' Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea. | ||
* '''Vision Abnormalities:''' Some patients may experience blurred or double vision. | * '''Vision Abnormalities:''' Some patients may experience blurred or double vision. | ||
== Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics == | == Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics == | ||
While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population. | While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population. | ||
* '''Age Demographics:''' Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10. | * '''Age Demographics:''' Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10. | ||
* '''Significance:''' It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children. | * '''Significance:''' It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children. | ||
[[File:CT brain scan of child with medulloblastoma and resulting hydrocephalus.jpg|left|thumb|250px|Illustration highlighting different pediatric brain tumors, including medulloblastoma.]] | |||
[[File:CT brain scan of child with medulloblastoma and resulting hydrocephalus.jpg|thumb | |||
== Diagnosis and Treatment == | == Diagnosis and Treatment == | ||
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes. | Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes. | ||
=== Diagnostic Tools === | === Diagnostic Tools === | ||
* [[MRI]] and [[CT scan]]: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor. | * [[MRI]] and [[CT scan]]: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor. | ||
* '''Biopsy:''' A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature. | * '''Biopsy:''' A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature. | ||
=== Treatment Modalities === | === Treatment Modalities === | ||
* '''Surgery:''' Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment. | * '''Surgery:''' Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment. | ||
* '''Radiation Therapy:''' Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells. | * '''Radiation Therapy:''' Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells. | ||
* '''Chemotherapy:''' Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence. | * '''Chemotherapy:''' Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence. | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals. | Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals. | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:54, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Medulloblastoma | |
|---|---|
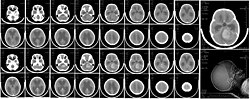
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, ataxia, dizziness, vision problems |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, cerebellar mutism syndrome |
| Onset | Most common in children |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | Classic, Desmoplastic/nodular, Large cell/anaplastic, Medulloblastoma with extensive nodularity |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Genetic syndromes (e.g., Gorlin syndrome, Turcot syndrome) |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Ependymoma, astrocytoma, brainstem glioma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on age, tumor subtype, and extent of disease |
| Frequency | Most common malignant brain tumor in children |
| Deaths | N/A |
Medulloblastoma: An Introduction[edit]
Medulloblastoma is a malignant tumor primarily affecting the central nervous system. Though it can manifest in adults, it is predominantly observed in children, making it a significant pediatric concern.

Anatomy and Localization[edit]
Medulloblastoma predominantly arises in the cerebellum, an area of the brain responsible for various functions.
Cerebellum: The Origin Site[edit]
- The cerebellum is situated at the base of the brain and plays a pivotal role in regulating balance, posture, and coordination.
- Tumors in this area can disrupt these functions, leading to noticeable neurological symptoms.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Children or adults presenting with medulloblastoma often exhibit certain symptoms that stem from the tumor's location and growth.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Due to the cerebellum's function, patients might display challenges with walking or performing coordinated movements.
- Headaches and Nausea: Increased intracranial pressure from tumor growth can lead to persistent headaches and bouts of nausea.
- Vision Abnormalities: Some patients may experience blurred or double vision.
Epidemiology: A Focus on Pediatrics[edit]
While medulloblastomas can be found in individuals of any age, they have a notable prevalence in the pediatric population.
- Age Demographics: Most commonly diagnosed in children under the age of 10.
- Significance: It stands as one of the most frequent malignant brain tumors in children.

Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better prognostic outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools[edit]
- MRI and CT scan: These imaging tools are vital in visualizing the tumor.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample helps determine the tumor's exact nature.
Treatment Modalities[edit]
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor is typically the first line of treatment.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used post-surgery to target residual cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Employed to kill cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion[edit]
Medulloblastoma, while being a prominent pediatric malignancy, requires comprehensive understanding and multidisciplinary care for effective management. Advancements in research and medical interventions continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for affected individuals.


