Parasitic disease: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Parasitic disease | |||
| image = [[File:Malaria.jpg|250px]] | |||
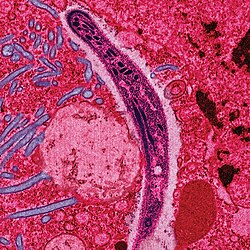
| caption = ''[[Plasmodium]]'' parasites in a blood smear, the cause of [[malaria]] | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = Varies by parasite; may include [[fever]], [[fatigue (medical)|fatigue]], [[gastrointestinal symptoms]], [[skin rash]] | |||
| complications = [[Anemia]], [[malnutrition]], [[organ damage]] | |||
| onset = Varies by parasite | |||
| duration = Acute or chronic | |||
| causes = [[Parasite]]s such as [[protozoa]], [[helminths]], and [[ectoparasites]] | |||
| risks = Poor sanitation, lack of clean water, exposure to vectors | |||
| diagnosis = [[Microscopy]], [[serology]], [[molecular diagnostics]] | |||
| prevention = [[Vector control]], [[sanitation]], [[prophylactic medication]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antiparasitic drugs]], [[supportive care]] | |||
| frequency = Common in tropical and subtropical regions | |||
}} | |||
{{short description|A disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes}} | {{short description|A disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes}} | ||
'''Parasitic diseases''' are infections caused by parasites, which are organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive their nutrients at the host's expense. One of the most well-known parasitic diseases is [[malaria]], caused by the [[Plasmodium]] parasite and transmitted by the bite of infected [[Anopheles]] mosquitoes. | '''Parasitic diseases''' are infections caused by parasites, which are organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive their nutrients at the host's expense. One of the most well-known parasitic diseases is [[malaria]], caused by the [[Plasmodium]] parasite and transmitted by the bite of infected [[Anopheles]] mosquitoes. | ||
==Types of Parasitic Diseases== | ==Types of Parasitic Diseases== | ||
Parasitic diseases can be classified into three main types based on the type of parasite: | Parasitic diseases can be classified into three main types based on the type of parasite: | ||
===Protozoan Infections=== | ===Protozoan Infections=== | ||
Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can cause diseases such as malaria, [[amoebiasis]], and [[giardiasis]]. Malaria, in particular, is a significant global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. | Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can cause diseases such as malaria, [[amoebiasis]], and [[giardiasis]]. Malaria, in particular, is a significant global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. | ||
===Helminth Infections=== | ===Helminth Infections=== | ||
Helminths are multicellular parasitic worms, including [[roundworms]], [[tapeworms]], and [[flukes]]. These parasites can cause diseases such as [[schistosomiasis]], [[ascariasis]], and [[hookworm infection]]. | Helminths are multicellular parasitic worms, including [[roundworms]], [[tapeworms]], and [[flukes]]. These parasites can cause diseases such as [[schistosomiasis]], [[ascariasis]], and [[hookworm infection]]. | ||
===Ectoparasitic Infections=== | ===Ectoparasitic Infections=== | ||
Ectoparasites live on the surface of the host and include organisms such as [[lice]], [[fleas]], and [[mites]]. They can cause conditions like [[scabies]] and [[pediculosis]]. | Ectoparasites live on the surface of the host and include organisms such as [[lice]], [[fleas]], and [[mites]]. They can cause conditions like [[scabies]] and [[pediculosis]]. | ||
==Transmission== | ==Transmission== | ||
Parasitic diseases are transmitted through various routes, including: | Parasitic diseases are transmitted through various routes, including: | ||
* '''Vector-borne transmission''': As seen in malaria, where mosquitoes act as vectors. | * '''Vector-borne transmission''': As seen in malaria, where mosquitoes act as vectors. | ||
* '''Fecal-oral transmission''': Common in protozoan infections like amoebiasis. | * '''Fecal-oral transmission''': Common in protozoan infections like amoebiasis. | ||
* '''Direct contact''': Seen in ectoparasitic infections like scabies. | * '''Direct contact''': Seen in ectoparasitic infections like scabies. | ||
* '''Consumption of contaminated food or water''': A route for many helminth infections. | * '''Consumption of contaminated food or water''': A route for many helminth infections. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of parasitic diseases vary widely depending on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include: | The symptoms of parasitic diseases vary widely depending on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include: | ||
* Fever and chills (common in malaria) | * Fever and chills (common in malaria) | ||
* Abdominal pain and diarrhea (common in amoebiasis and giardiasis) | * Abdominal pain and diarrhea (common in amoebiasis and giardiasis) | ||
* Skin rashes and itching (common in scabies) | * Skin rashes and itching (common in scabies) | ||
* Fatigue and weight loss (common in helminth infections) | * Fatigue and weight loss (common in helminth infections) | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of parasitic diseases often involves: | Diagnosis of parasitic diseases often involves: | ||
* '''Microscopic examination''': Identifying parasites in blood, stool, or tissue samples. | * '''Microscopic examination''': Identifying parasites in blood, stool, or tissue samples. | ||
* '''Serological tests''': Detecting antibodies or antigens related to the parasite. | * '''Serological tests''': Detecting antibodies or antigens related to the parasite. | ||
* '''Molecular methods''': Using PCR to detect parasite DNA. | * '''Molecular methods''': Using PCR to detect parasite DNA. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment depends on the specific parasite involved and may include: | Treatment depends on the specific parasite involved and may include: | ||
* '''Antimalarial drugs''': Such as chloroquine or artemisinin-based combination therapies for malaria. | * '''Antimalarial drugs''': Such as chloroquine or artemisinin-based combination therapies for malaria. | ||
* '''Antiprotozoal medications''': Such as metronidazole for amoebiasis. | * '''Antiprotozoal medications''': Such as metronidazole for amoebiasis. | ||
* '''Anthelmintic drugs''': Such as albendazole or mebendazole for helminth infections. | * '''Anthelmintic drugs''': Such as albendazole or mebendazole for helminth infections. | ||
* '''Topical treatments''': For ectoparasitic infections like scabies. | * '''Topical treatments''': For ectoparasitic infections like scabies. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventive measures include: | Preventive measures include: | ||
* '''Vector control''': Using insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying to prevent malaria. | * '''Vector control''': Using insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying to prevent malaria. | ||
* '''Improved sanitation''': To prevent fecal-oral transmission of parasites. | * '''Improved sanitation''': To prevent fecal-oral transmission of parasites. | ||
* '''Health education''': Promoting hygiene and safe food practices. | * '''Health education''': Promoting hygiene and safe food practices. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Malaria]] | * [[Malaria]] | ||
* [[Protozoan infection]] | * [[Protozoan infection]] | ||
* [[Helminthiasis]] | * [[Helminthiasis]] | ||
* [[Ectoparasite]] | * [[Ectoparasite]] | ||
[[Category:Parasitic diseases]] | [[Category:Parasitic diseases]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:56, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Parasitic disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Varies by parasite; may include fever, fatigue, gastrointestinal symptoms, skin rash |
| Complications | Anemia, malnutrition, organ damage |
| Onset | Varies by parasite |
| Duration | Acute or chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Parasites such as protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites |
| Risks | Poor sanitation, lack of clean water, exposure to vectors |
| Diagnosis | Microscopy, serology, molecular diagnostics |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Vector control, sanitation, prophylactic medication |
| Treatment | Antiparasitic drugs, supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in tropical and subtropical regions |
| Deaths | N/A |
A disease caused by parasites transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes
Parasitic diseases are infections caused by parasites, which are organisms that live on or in a host organism and derive their nutrients at the host's expense. One of the most well-known parasitic diseases is malaria, caused by the Plasmodium parasite and transmitted by the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Types of Parasitic Diseases[edit]
Parasitic diseases can be classified into three main types based on the type of parasite:
Protozoan Infections[edit]
Protozoa are single-celled organisms that can cause diseases such as malaria, amoebiasis, and giardiasis. Malaria, in particular, is a significant global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions.
Helminth Infections[edit]
Helminths are multicellular parasitic worms, including roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes. These parasites can cause diseases such as schistosomiasis, ascariasis, and hookworm infection.
Ectoparasitic Infections[edit]
Ectoparasites live on the surface of the host and include organisms such as lice, fleas, and mites. They can cause conditions like scabies and pediculosis.
Transmission[edit]
Parasitic diseases are transmitted through various routes, including:
- Vector-borne transmission: As seen in malaria, where mosquitoes act as vectors.
- Fecal-oral transmission: Common in protozoan infections like amoebiasis.
- Direct contact: Seen in ectoparasitic infections like scabies.
- Consumption of contaminated food or water: A route for many helminth infections.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of parasitic diseases vary widely depending on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills (common in malaria)
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea (common in amoebiasis and giardiasis)
- Skin rashes and itching (common in scabies)
- Fatigue and weight loss (common in helminth infections)
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of parasitic diseases often involves:
- Microscopic examination: Identifying parasites in blood, stool, or tissue samples.
- Serological tests: Detecting antibodies or antigens related to the parasite.
- Molecular methods: Using PCR to detect parasite DNA.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment depends on the specific parasite involved and may include:
- Antimalarial drugs: Such as chloroquine or artemisinin-based combination therapies for malaria.
- Antiprotozoal medications: Such as metronidazole for amoebiasis.
- Anthelmintic drugs: Such as albendazole or mebendazole for helminth infections.
- Topical treatments: For ectoparasitic infections like scabies.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures include:
- Vector control: Using insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying to prevent malaria.
- Improved sanitation: To prevent fecal-oral transmission of parasites.
- Health education: Promoting hygiene and safe food practices.