Hemifacial microsomia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hemifacial microsomia | |||
| image = [[File:Bialateral_hemifacial_microsomia.JPG|250px]] | |||
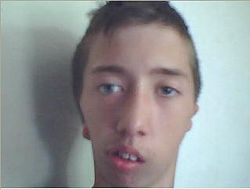
| caption = Bilateral hemifacial microsomia | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]], [[Otolaryngology]], [[Plastic surgery]] | |||
| synonyms = [[First and second branchial arch syndrome]], [[Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Facial asymmetry]], [[Microtia]], [[Mandibular hypoplasia]], [[Hearing loss]] | |||
| complications = [[Breathing difficulties]], [[Feeding difficulties]], [[Speech disorders]] | |||
| onset = [[Congenital]] | |||
| duration = [[Lifelong]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutations]], [[Environmental factors]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]], [[Maternal diabetes]], [[Multiple gestation]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[Imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Treacher Collins syndrome]], [[Goldenhar syndrome]], [[Craniofacial microsomia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical intervention]], [[Hearing aids]], [[Speech therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Varies]] | |||
| frequency = 1 in 3,500 to 1 in 5,600 live births | |||
| deaths = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Hemifacial microsomia''' (HFM) is a congenital disorder characterized by asymmetry of the face due to underdevelopment of one side. The condition can affect the ear, mouth, and jaw, and in some cases, the eye and neck. The severity of the condition varies widely among individuals, ranging from mild to severe. | '''Hemifacial microsomia''' (HFM) is a congenital disorder characterized by asymmetry of the face due to underdevelopment of one side. The condition can affect the ear, mouth, and jaw, and in some cases, the eye and neck. The severity of the condition varies widely among individuals, ranging from mild to severe. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
The exact cause of HFM is unknown, but it is believed to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Some researchers suggest that a disruption in blood flow to the face during early development may play a role. | The exact cause of HFM is unknown, but it is believed to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Some researchers suggest that a disruption in blood flow to the face during early development may play a role. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of HFM can vary greatly among individuals. They may include: | The symptoms of HFM can vary greatly among individuals. They may include: | ||
* Underdevelopment of one side of the face | * Underdevelopment of one side of the face | ||
* Malformation of the ear | * Malformation of the ear | ||
| Line 15: | Line 30: | ||
* Eye abnormalities | * Eye abnormalities | ||
* Neck abnormalities | * Neck abnormalities | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of HFM is typically made based on a physical examination and the individual's medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI may be used to assess the severity of the condition and plan treatment. | Diagnosis of HFM is typically made based on a physical examination and the individual's medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI may be used to assess the severity of the condition and plan treatment. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for HFM is typically multidisciplinary, involving a team of specialists including a plastic surgeon, oral surgeon, orthodontist, audiologist, and speech therapist. The goal of treatment is to improve function and appearance. Treatment options may include surgery, orthodontic treatment, and speech therapy. | Treatment for HFM is typically multidisciplinary, involving a team of specialists including a plastic surgeon, oral surgeon, orthodontist, audiologist, and speech therapist. The goal of treatment is to improve function and appearance. Treatment options may include surgery, orthodontic treatment, and speech therapy. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Craniofacial abnormalities]] | * [[Craniofacial abnormalities]] | ||
* [[Congenital disorders]] | * [[Congenital disorders]] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 41: | ||
* [[Audiology]] | * [[Audiology]] | ||
* [[Speech therapy]] | * [[Speech therapy]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders]] | [[Category:Congenital disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Craniofacial abnormalities]] | [[Category:Craniofacial abnormalities]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:24, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hemifacial microsomia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | First and second branchial arch syndrome, Oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Facial asymmetry, Microtia, Mandibular hypoplasia, Hearing loss |
| Complications | Breathing difficulties, Feeding difficulties, Speech disorders |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, Environmental factors |
| Risks | Family history, Maternal diabetes, Multiple gestation |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, Imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Treacher Collins syndrome, Goldenhar syndrome, Craniofacial microsomia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention, Hearing aids, Speech therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies |
| Frequency | 1 in 3,500 to 1 in 5,600 live births |
| Deaths | Rare |
Hemifacial microsomia (HFM) is a congenital disorder characterized by asymmetry of the face due to underdevelopment of one side. The condition can affect the ear, mouth, and jaw, and in some cases, the eye and neck. The severity of the condition varies widely among individuals, ranging from mild to severe.
Causes[edit]
The exact cause of HFM is unknown, but it is believed to be multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Some researchers suggest that a disruption in blood flow to the face during early development may play a role.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of HFM can vary greatly among individuals. They may include:
- Underdevelopment of one side of the face
- Malformation of the ear
- Dental abnormalities
- Cleft lip or palate
- Eye abnormalities
- Neck abnormalities
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of HFM is typically made based on a physical examination and the individual's medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI may be used to assess the severity of the condition and plan treatment.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for HFM is typically multidisciplinary, involving a team of specialists including a plastic surgeon, oral surgeon, orthodontist, audiologist, and speech therapist. The goal of treatment is to improve function and appearance. Treatment options may include surgery, orthodontic treatment, and speech therapy.
See also[edit]
- Craniofacial abnormalities
- Congenital disorders
- Plastic surgery
- Orthodontics
- Audiology
- Speech therapy
References[edit]
<references />


