Hematosalpinx: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hematosalpinx | |||
| image = [[File:Ectopic_pregnancy_on_laparoscopy.png|250px]] | |||
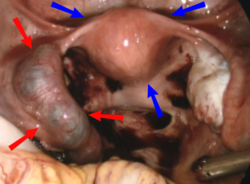
| caption = Laparoscopic view of an ectopic pregnancy, which can cause hematosalpinx | |||
| field = [[Gynecology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pelvic pain]], [[abnormal uterine bleeding]] | |||
| complications = [[Infertility]], [[ectopic pregnancy]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Ectopic pregnancy]], [[endometriosis]], [[tubal surgery]] | |||
| risks = [[Pelvic inflammatory disease]], [[previous ectopic pregnancy]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ultrasound]], [[laparoscopy]] | |||
| differential = [[Ovarian cyst]], [[pelvic inflammatory disease]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgery]], [[medication]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Hematosalpinx''' is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of blood within the [[fallopian tubes]], which are part of the female reproductive system. This condition can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may result in complications affecting fertility and overall reproductive health. | '''Hematosalpinx''' is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of blood within the [[fallopian tubes]], which are part of the female reproductive system. This condition can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may result in complications affecting fertility and overall reproductive health. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Hematosalpinx is often caused by [[pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)]], [[endometriosis]], or [[ectopic pregnancy]]. These conditions can lead to the blockage of the fallopian tube, preventing blood from exiting the body during menstruation and leading to its accumulation. Other causes may include [[tubal surgery]], infections, or tumors. | Hematosalpinx is often caused by [[pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)]], [[endometriosis]], or [[ectopic pregnancy]]. These conditions can lead to the blockage of the fallopian tube, preventing blood from exiting the body during menstruation and leading to its accumulation. Other causes may include [[tubal surgery]], infections, or tumors. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The symptoms of hematosalpinx can vary depending on the underlying cause but typically include pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, and in some cases, symptoms of an infection such as fever or unusual vaginal discharge. The pain is often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation on one side of the pelvis. | The symptoms of hematosalpinx can vary depending on the underlying cause but typically include pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, and in some cases, symptoms of an infection such as fever or unusual vaginal discharge. The pain is often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation on one side of the pelvis. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of hematosalpinx involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. [[Ultrasound]] is commonly used to visualize the fallopian tubes and detect the presence of fluid accumulation. In some cases, a [[hysterosalpingography]] (HSG) or [[laparoscopy]] may be performed to further evaluate the condition and its cause. | Diagnosis of hematosalpinx involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. [[Ultrasound]] is commonly used to visualize the fallopian tubes and detect the presence of fluid accumulation. In some cases, a [[hysterosalpingography]] (HSG) or [[laparoscopy]] may be performed to further evaluate the condition and its cause. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for hematosalpinx focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the blood accumulation. In cases where infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed. If the condition is due to endometriosis or ectopic pregnancy, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the blockage or affected tissue. In severe cases, removal of the affected fallopian tube ([[salpingectomy]]) may be recommended to prevent further complications. | Treatment for hematosalpinx focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the blood accumulation. In cases where infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed. If the condition is due to endometriosis or ectopic pregnancy, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the blockage or affected tissue. In severe cases, removal of the affected fallopian tube ([[salpingectomy]]) may be recommended to prevent further complications. | ||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
If left untreated, hematosalpinx can lead to [[infertility]], due to damage to the fallopian tubes or the development of scar tissue. Additionally, the condition can increase the risk of future ectopic pregnancies, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube. | If left untreated, hematosalpinx can lead to [[infertility]], due to damage to the fallopian tubes or the development of scar tissue. Additionally, the condition can increase the risk of future ectopic pregnancies, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventing hematosalpinx involves managing risk factors for its underlying causes. Regular medical check-ups, practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of PID, and managing conditions like endometriosis can help lower the risk of developing hematosalpinx. | Preventing hematosalpinx involves managing risk factors for its underlying causes. Regular medical check-ups, practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of PID, and managing conditions like endometriosis can help lower the risk of developing hematosalpinx. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Ectopic pregnancy]] | * [[Ectopic pregnancy]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 35: | ||
* [[Pelvic inflammatory disease]] | * [[Pelvic inflammatory disease]] | ||
* [[Salpingectomy]] | * [[Salpingectomy]] | ||
[[Category:Gynecological conditions]] | [[Category:Gynecological conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Reproductive system]] | [[Category:Reproductive system]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions related to menstruation]] | [[Category:Medical conditions related to menstruation]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:21, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hematosalpinx | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pelvic pain, abnormal uterine bleeding |
| Complications | Infertility, ectopic pregnancy |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, tubal surgery |
| Risks | Pelvic inflammatory disease, previous ectopic pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, laparoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Ovarian cyst, pelvic inflammatory disease |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, medication |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hematosalpinx is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of blood within the fallopian tubes, which are part of the female reproductive system. This condition can lead to significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may result in complications affecting fertility and overall reproductive health.
Causes[edit]
Hematosalpinx is often caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or ectopic pregnancy. These conditions can lead to the blockage of the fallopian tube, preventing blood from exiting the body during menstruation and leading to its accumulation. Other causes may include tubal surgery, infections, or tumors.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of hematosalpinx can vary depending on the underlying cause but typically include pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal bleeding, and in some cases, symptoms of an infection such as fever or unusual vaginal discharge. The pain is often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation on one side of the pelvis.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of hematosalpinx involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Ultrasound is commonly used to visualize the fallopian tubes and detect the presence of fluid accumulation. In some cases, a hysterosalpingography (HSG) or laparoscopy may be performed to further evaluate the condition and its cause.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for hematosalpinx focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the blood accumulation. In cases where infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed. If the condition is due to endometriosis or ectopic pregnancy, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the blockage or affected tissue. In severe cases, removal of the affected fallopian tube (salpingectomy) may be recommended to prevent further complications.
Complications[edit]
If left untreated, hematosalpinx can lead to infertility, due to damage to the fallopian tubes or the development of scar tissue. Additionally, the condition can increase the risk of future ectopic pregnancies, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing hematosalpinx involves managing risk factors for its underlying causes. Regular medical check-ups, practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of PID, and managing conditions like endometriosis can help lower the risk of developing hematosalpinx.
See Also[edit]
