Fungal sinusitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Fungal sinusitis | |||
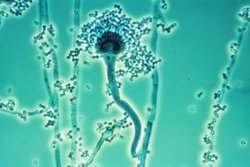
| image = [[File:Aspergillus.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = ''[[Aspergillus]]'' species, a common cause of fungal sinusitis | |||
| field = [[Otorhinolaryngology]] | |||
| synonyms = Fungal rhinosinusitis | |||
| symptoms = [[Nasal congestion]], [[facial pain]], [[headache]], [[fever]], [[nasal discharge]] | |||
| complications = [[Orbital cellulitis]], [[intracranial complications]], [[bone erosion]] | |||
| onset = Varies depending on type (acute or chronic) | |||
| duration = Can be acute or chronic | |||
| types = [[Allergic fungal sinusitis]], [[chronic indolent sinusitis]], [[fungal ball]], [[acute invasive fungal sinusitis]] | |||
| causes = [[Fungal infection]] by species such as ''[[Aspergillus]]'', ''[[Mucor]]'', ''[[Rhizopus]]'' | |||
| risks = [[Immunocompromised]] state, [[diabetes mellitus]], [[chronic sinusitis]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], [[nasal endoscopy]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Bacterial sinusitis]], [[viral sinusitis]], [[nasal polyps]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antifungal medication]], [[surgery]], [[corticosteroids]] | |||
| medication = [[Amphotericin B]], [[voriconazole]], [[itraconazole]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; better with early diagnosis and treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare, but more common in [[immunocompromised]] individuals | |||
}} | |||
'''Fungal sinusitis''' is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the [[sinus]] lining due to a fungal infection. It is a relatively uncommon form of [[sinusitis]] and can be classified into two main categories: invasive and non-invasive. Invasive fungal sinusitis is a serious condition that typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with [[diabetes mellitus]], [[cancer]], or [[HIV/AIDS]]. Non-invasive fungal sinusitis, on the other hand, generally occurs in individuals with normal immune systems and is further divided into allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS) and fungal ball. | '''Fungal sinusitis''' is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the [[sinus]] lining due to a fungal infection. It is a relatively uncommon form of [[sinusitis]] and can be classified into two main categories: invasive and non-invasive. Invasive fungal sinusitis is a serious condition that typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with [[diabetes mellitus]], [[cancer]], or [[HIV/AIDS]]. Non-invasive fungal sinusitis, on the other hand, generally occurs in individuals with normal immune systems and is further divided into allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS) and fungal ball. | ||
== Causes and Risk Factors == | == Causes and Risk Factors == | ||
Fungal sinusitis is caused by the inhalation of fungal spores, which can then infect the sinus cavities. The most common fungi associated with this condition include species from the genera ''[[Aspergillus]]'', ''[[Fusarium]]'', and ''[[Mucor]]''. Risk factors for developing fungal sinusitis include a weakened immune system, living in environments with high levels of fungal spores, previous sinus surgery, and the use of immunosuppressive medications. | Fungal sinusitis is caused by the inhalation of fungal spores, which can then infect the sinus cavities. The most common fungi associated with this condition include species from the genera ''[[Aspergillus]]'', ''[[Fusarium]]'', and ''[[Mucor]]''. Risk factors for developing fungal sinusitis include a weakened immune system, living in environments with high levels of fungal spores, previous sinus surgery, and the use of immunosuppressive medications. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of fungal sinusitis can vary depending on the type of infection but generally include chronic nasal congestion, nasal discharge (which may be thick and contain black material in cases of invasive fungal sinusitis), facial pain or pressure, reduced sense of smell, and headaches. In severe cases of invasive fungal sinusitis, symptoms may also include fever, eye swelling, and vision changes. | Symptoms of fungal sinusitis can vary depending on the type of infection but generally include chronic nasal congestion, nasal discharge (which may be thick and contain black material in cases of invasive fungal sinusitis), facial pain or pressure, reduced sense of smell, and headaches. In severe cases of invasive fungal sinusitis, symptoms may also include fever, eye swelling, and vision changes. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of fungal sinusitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies such as [[Computed Tomography (CT) scan|CT scans]] or [[Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)|MRI]], and laboratory tests. Nasal endoscopy may be performed to obtain samples for fungal cultures and histopathological examination. Identifying the specific type of fungus is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. | Diagnosis of fungal sinusitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies such as [[Computed Tomography (CT) scan|CT scans]] or [[Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)|MRI]], and laboratory tests. Nasal endoscopy may be performed to obtain samples for fungal cultures and histopathological examination. Identifying the specific type of fungus is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for fungal sinusitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Non-invasive forms, such as allergic fungal sinusitis and fungal ball, are typically treated with surgery to remove the fungal mass and antifungal medications. Invasive fungal sinusitis requires aggressive treatment with intravenous antifungal medications and, in some cases, surgery to remove infected tissue. Long-term management may include the use of oral antifungal medications to prevent recurrence. | Treatment for fungal sinusitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Non-invasive forms, such as allergic fungal sinusitis and fungal ball, are typically treated with surgery to remove the fungal mass and antifungal medications. Invasive fungal sinusitis requires aggressive treatment with intravenous antifungal medications and, in some cases, surgery to remove infected tissue. Long-term management may include the use of oral antifungal medications to prevent recurrence. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Preventive measures for fungal sinusitis include avoiding environments with high concentrations of fungal spores, such as compost piles and moldy spaces. Individuals with weakened immune systems should take additional precautions, such as wearing masks in potentially contaminated areas and ensuring that indoor air is clean and well-filtered. | Preventive measures for fungal sinusitis include avoiding environments with high concentrations of fungal spores, such as compost piles and moldy spaces. Individuals with weakened immune systems should take additional precautions, such as wearing masks in potentially contaminated areas and ensuring that indoor air is clean and well-filtered. | ||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Granuloma_mac.jpg|Granuloma formation in fungal sinusitis | |||
File:MRI-Philips.JPG|MRI scan showing fungal sinusitis | |||
File:Voriconazole_ball-and-stick_model.png|Voriconazole, an antifungal medication used in treatment | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Sinusitis]] | * [[Sinusitis]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Aspergillosis]] | * [[Aspergillosis]] | ||
* [[Mucormycosis]] | * [[Mucormycosis]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | [[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious diseases]] | [[Category:Infectious diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Mycoses]] | [[Category:Mycoses]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:33, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Fungal sinusitis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Fungal rhinosinusitis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Nasal congestion, facial pain, headache, fever, nasal discharge |
| Complications | Orbital cellulitis, intracranial complications, bone erosion |
| Onset | Varies depending on type (acute or chronic) |
| Duration | Can be acute or chronic |
| Types | Allergic fungal sinusitis, chronic indolent sinusitis, fungal ball, acute invasive fungal sinusitis |
| Causes | Fungal infection by species such as Aspergillus, Mucor, Rhizopus |
| Risks | Immunocompromised state, diabetes mellitus, chronic sinusitis |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, MRI, nasal endoscopy, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Bacterial sinusitis, viral sinusitis, nasal polyps |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Antifungal medication, surgery, corticosteroids |
| Medication | Amphotericin B, voriconazole, itraconazole |
| Prognosis | Varies; better with early diagnosis and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare, but more common in immunocompromised individuals |
| Deaths | N/A |
Fungal sinusitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the sinus lining due to a fungal infection. It is a relatively uncommon form of sinusitis and can be classified into two main categories: invasive and non-invasive. Invasive fungal sinusitis is a serious condition that typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes mellitus, cancer, or HIV/AIDS. Non-invasive fungal sinusitis, on the other hand, generally occurs in individuals with normal immune systems and is further divided into allergic fungal sinusitis (AFS) and fungal ball.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit]
Fungal sinusitis is caused by the inhalation of fungal spores, which can then infect the sinus cavities. The most common fungi associated with this condition include species from the genera Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Mucor. Risk factors for developing fungal sinusitis include a weakened immune system, living in environments with high levels of fungal spores, previous sinus surgery, and the use of immunosuppressive medications.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of fungal sinusitis can vary depending on the type of infection but generally include chronic nasal congestion, nasal discharge (which may be thick and contain black material in cases of invasive fungal sinusitis), facial pain or pressure, reduced sense of smell, and headaches. In severe cases of invasive fungal sinusitis, symptoms may also include fever, eye swelling, and vision changes.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of fungal sinusitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI, and laboratory tests. Nasal endoscopy may be performed to obtain samples for fungal cultures and histopathological examination. Identifying the specific type of fungus is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for fungal sinusitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Non-invasive forms, such as allergic fungal sinusitis and fungal ball, are typically treated with surgery to remove the fungal mass and antifungal medications. Invasive fungal sinusitis requires aggressive treatment with intravenous antifungal medications and, in some cases, surgery to remove infected tissue. Long-term management may include the use of oral antifungal medications to prevent recurrence.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures for fungal sinusitis include avoiding environments with high concentrations of fungal spores, such as compost piles and moldy spaces. Individuals with weakened immune systems should take additional precautions, such as wearing masks in potentially contaminated areas and ensuring that indoor air is clean and well-filtered.
Gallery[edit]
-
Granuloma formation in fungal sinusitis
-
MRI scan showing fungal sinusitis
-
Voriconazole, an antifungal medication used in treatment
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>


