Chance fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Chance fracture | |||
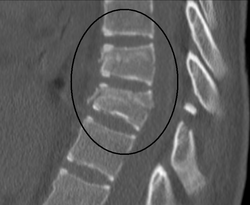
| image = [[File:PchancefracCT.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = CT scan showing a Chance fracture | |||
| synonyms = Seat belt fracture | |||
| specialty = [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Back pain]], [[neurological deficits]] | |||
| complications = [[Spinal cord injury]], [[paralysis]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, typically due to trauma | |||
| causes = [[Flexion-distraction injury]], often from [[motor vehicle accident]] | |||
| risks = Improper use of [[seat belt]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Compression fracture]], [[burst fracture]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical fixation]], [[bracing]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, depending on severity and presence of neurological injury | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:PchancefracX.png|X-ray showing chance fracture|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Chance fracture''' is a type of [[vertebral fracture]] that occurs in the [[spine]]. It is named after the British surgeon, G.Q. Chance, who first described it in 1948. This fracture is often associated with high-speed accidents, particularly motor vehicle accidents where the person is wearing a seatbelt. | '''Chance fracture''' is a type of [[vertebral fracture]] that occurs in the [[spine]]. It is named after the British surgeon, G.Q. Chance, who first described it in 1948. This fracture is often associated with high-speed accidents, particularly motor vehicle accidents where the person is wearing a seatbelt. | ||
==Mechanism of Injury== | ==Mechanism of Injury== | ||
A Chance fracture is a flexion-distraction injury that occurs when the spine is suddenly forced forward while the pelvis is stabilized. This is commonly seen in motor vehicle accidents where the upper body is thrown forward while the lower body is restrained by a lap seatbelt. The force of the forward motion causes the vertebrae in the spine to pull apart, or distract, resulting in a horizontal fracture through the vertebral body, pedicles, and spinous process. | A Chance fracture is a flexion-distraction injury that occurs when the spine is suddenly forced forward while the pelvis is stabilized. This is commonly seen in motor vehicle accidents where the upper body is thrown forward while the lower body is restrained by a lap seatbelt. The force of the forward motion causes the vertebrae in the spine to pull apart, or distract, resulting in a horizontal fracture through the vertebral body, pedicles, and spinous process. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with a Chance fracture often present with severe back pain, particularly in the mid to lower back region. They may also have abdominal pain due to associated intra-abdominal injuries. On physical examination, there may be visible bruising or a seatbelt sign across the abdomen. Neurological deficits are rare as the spinal cord is usually not involved. | Patients with a Chance fracture often present with severe back pain, particularly in the mid to lower back region. They may also have abdominal pain due to associated intra-abdominal injuries. On physical examination, there may be visible bruising or a seatbelt sign across the abdomen. Neurological deficits are rare as the spinal cord is usually not involved. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of a Chance fracture is typically made through imaging studies. An [[X-ray]] of the spine may show a horizontal fracture line through the vertebral body. However, a [[Computed Tomography|CT scan]] is more sensitive and can better visualize the fracture and any associated injuries. In some cases, a [[Magnetic Resonance Imaging|MRI]] may be used to assess for any soft tissue injuries. | The diagnosis of a Chance fracture is typically made through imaging studies. An [[X-ray]] of the spine may show a horizontal fracture line through the vertebral body. However, a [[Computed Tomography|CT scan]] is more sensitive and can better visualize the fracture and any associated injuries. In some cases, a [[Magnetic Resonance Imaging|MRI]] may be used to assess for any soft tissue injuries. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment of a Chance fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and any associated injuries. Non-operative treatment may include bracing and physical therapy. However, in cases of unstable fractures or fractures with associated neurological deficits, surgical intervention may be required. This typically involves spinal fusion and fixation to stabilize the spine. | The treatment of a Chance fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and any associated injuries. Non-operative treatment may include bracing and physical therapy. However, in cases of unstable fractures or fractures with associated neurological deficits, surgical intervention may be required. This typically involves spinal fusion and fixation to stabilize the spine. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for a Chance fracture is generally good with appropriate treatment. Most patients are able to return to normal activities after a period of rehabilitation. However, complications can occur, including chronic back pain, spinal deformity, and neurological deficits. | The prognosis for a Chance fracture is generally good with appropriate treatment. Most patients are able to return to normal activities after a period of rehabilitation. However, complications can occur, including chronic back pain, spinal deformity, and neurological deficits. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Spinal fracture]] | * [[Spinal fracture]] | ||
* [[Seatbelt sign]] | * [[Seatbelt sign]] | ||
* [[Spinal fusion]] | * [[Spinal fusion]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic problems]] | [[Category:Orthopedic problems]] | ||
[[Category:Injuries]] | [[Category:Injuries]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Chance fracture | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Seat belt fracture |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery |
| Symptoms | Back pain, neurological deficits |
| Complications | Spinal cord injury, paralysis |
| Onset | Sudden, typically due to trauma |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Flexion-distraction injury, often from motor vehicle accident |
| Risks | Improper use of seat belt |
| Diagnosis | X-ray, CT scan, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Compression fracture, burst fracture |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical fixation, bracing, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies, depending on severity and presence of neurological injury |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Chance fracture is a type of vertebral fracture that occurs in the spine. It is named after the British surgeon, G.Q. Chance, who first described it in 1948. This fracture is often associated with high-speed accidents, particularly motor vehicle accidents where the person is wearing a seatbelt.
Mechanism of Injury[edit]
A Chance fracture is a flexion-distraction injury that occurs when the spine is suddenly forced forward while the pelvis is stabilized. This is commonly seen in motor vehicle accidents where the upper body is thrown forward while the lower body is restrained by a lap seatbelt. The force of the forward motion causes the vertebrae in the spine to pull apart, or distract, resulting in a horizontal fracture through the vertebral body, pedicles, and spinous process.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with a Chance fracture often present with severe back pain, particularly in the mid to lower back region. They may also have abdominal pain due to associated intra-abdominal injuries. On physical examination, there may be visible bruising or a seatbelt sign across the abdomen. Neurological deficits are rare as the spinal cord is usually not involved.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of a Chance fracture is typically made through imaging studies. An X-ray of the spine may show a horizontal fracture line through the vertebral body. However, a CT scan is more sensitive and can better visualize the fracture and any associated injuries. In some cases, a MRI may be used to assess for any soft tissue injuries.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of a Chance fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and any associated injuries. Non-operative treatment may include bracing and physical therapy. However, in cases of unstable fractures or fractures with associated neurological deficits, surgical intervention may be required. This typically involves spinal fusion and fixation to stabilize the spine.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for a Chance fracture is generally good with appropriate treatment. Most patients are able to return to normal activities after a period of rehabilitation. However, complications can occur, including chronic back pain, spinal deformity, and neurological deficits.
See Also[edit]
