Brachial plexus injury: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Gray808.png|Brachial plexus | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Brachial plexus injury | |||
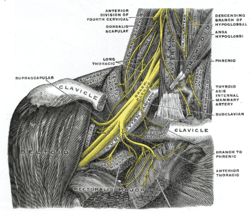
| image = [[File:Gray808.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = Brachial plexus | |||
| field = [[Neurology]], [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| synonyms = Brachial plexus neuropathy, Erb's palsy (upper trunk), Klumpke's palsy (lower trunk) | |||
| symptoms = [[Weakness]], [[numbness]], [[loss of function]] in the arm | |||
| complications = [[Chronic pain]], [[muscle atrophy]], [[paralysis]] | |||
| onset = At birth or due to trauma | |||
| duration = Varies, can be temporary or permanent | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[birth injury]], [[tumors]], [[inflammation]] | |||
| risks = [[Shoulder dystocia]], [[motorcycle accidents]], [[sports injuries]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[MRI]], [[nerve conduction study]] | |||
| differential = [[Cervical radiculopathy]], [[thoracic outlet syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[surgery]], [[nerve grafting]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, depends on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = 1-2 per 1,000 live births (for birth-related injuries) | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Brachial_plexus_1323.png|Brachial plexus anatomy|left|thumb]] | [[File:Brachial_plexus_1323.png|Brachial plexus anatomy|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Brachial_plexus_anterior_view_nerves.JPG|Anterior view of brachial plexus nerves|thumb]] | [[File:Brachial_plexus_anterior_view_nerves.JPG|Anterior view of brachial plexus nerves|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Figure_2._BPI_Traumatic_event.jpg|Traumatic event leading to BPI|left|thumb]] | [[File:Figure_2._BPI_Traumatic_event.jpg|Traumatic event leading to BPI|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Figure_3._Incidence_of_OBPP.jpg|Incidence of obstetric brachial plexus palsy|thumb]] | [[File:Figure_3._Incidence_of_OBPP.jpg|Incidence of obstetric brachial plexus palsy|left|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Figure_4._Motorcycles_and_BPI.jpg|Motorcycles and brachial plexus injury|thumb]] | [[File:Figure_4._Motorcycles_and_BPI.jpg|Motorcycles and brachial plexus injury|left|thumb]] | ||
A [[Brachial plexus injury]] is a type of [[nerve injury]] that occurs when the [[brachial plexus]] | A [[Brachial plexus injury]] is a type of [[nerve injury]] that occurs when the [[brachial plexus]]—a network of nerves that sends signals from the [[spinal cord]] to the [[shoulder]], [[arm]], and [[hand]]—is damaged. This can result in loss of muscle function and sensation in the affected area. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Brachial plexus injuries can occur as a result of [[shoulder trauma]], [[tumors]], or [[inflammation]]. However, the most common cause is [[birth injury]], which can occur when there is difficulty delivering the baby's shoulder, known as [[shoulder dystocia]]. | Brachial plexus injuries can occur as a result of [[shoulder trauma]], [[tumors]], or [[inflammation]]. However, the most common cause is [[birth injury]], which can occur when there is difficulty delivering the baby's shoulder, known as [[shoulder dystocia]]. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary greatly depending on the severity and location of the injury. They may include: | Symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary greatly depending on the severity and location of the injury. They may include: | ||
* [[Numbness]] or [[tingling]] in the arm or hand | * [[Numbness]] or [[tingling]] in the arm or hand | ||
* [[Weakness]] in the arm or hand | * [[Weakness]] in the arm or hand | ||
* Inability to use certain muscles in the hand or arm | * Inability to use certain muscles in the hand or arm | ||
* Severe [[pain]] | * Severe [[pain]] | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of a brachial plexus injury often involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may check for muscle weakness and feeling in the arm and hand. [[Imaging tests]], such as [[MRI]] and [[CT scans]], may also be used to help determine the location and extent of the damage. | Diagnosis of a brachial plexus injury often involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may check for muscle weakness and feeling in the arm and hand. [[Imaging tests]], such as [[MRI]] and [[CT scans]], may also be used to help determine the location and extent of the damage. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for brachial plexus injuries depends on the severity of the injury. Some mild injuries may heal on their own, while others may require [[physical therapy]], [[medication]], or [[surgery]]. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary. | Treatment for brachial plexus injuries depends on the severity of the injury. Some mild injuries may heal on their own, while others may require [[physical therapy]], [[medication]], or [[surgery]]. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for a brachial plexus injury depends on the severity and location of the injury, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Some patients may recover fully, while others may experience long-term complications, such as [[chronic pain]] and [[muscle weakness]]. | The prognosis for a brachial plexus injury depends on the severity and location of the injury, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Some patients may recover fully, while others may experience long-term complications, such as [[chronic pain]] and [[muscle weakness]]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Nerve injury]] | * [[Nerve injury]] | ||
* [[Shoulder dystocia]] | * [[Shoulder dystocia]] | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] | * [[Physical therapy]] | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Injuries]] | [[Category:Injuries]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:12, 4 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Brachial plexus injury | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Brachial plexus neuropathy, Erb's palsy (upper trunk), Klumpke's palsy (lower trunk) |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Weakness, numbness, loss of function in the arm |
| Complications | Chronic pain, muscle atrophy, paralysis |
| Onset | At birth or due to trauma |
| Duration | Varies, can be temporary or permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, birth injury, tumors, inflammation |
| Risks | Shoulder dystocia, motorcycle accidents, sports injuries |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, MRI, nerve conduction study |
| Differential diagnosis | Cervical radiculopathy, thoracic outlet syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, surgery, nerve grafting |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | 1-2 per 1,000 live births (for birth-related injuries) |
| Deaths | N/A |





A Brachial plexus injury is a type of nerve injury that occurs when the brachial plexus—a network of nerves that sends signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm, and hand—is damaged. This can result in loss of muscle function and sensation in the affected area.
Causes[edit]
Brachial plexus injuries can occur as a result of shoulder trauma, tumors, or inflammation. However, the most common cause is birth injury, which can occur when there is difficulty delivering the baby's shoulder, known as shoulder dystocia.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary greatly depending on the severity and location of the injury. They may include:
- Numbness or tingling in the arm or hand
- Weakness in the arm or hand
- Inability to use certain muscles in the hand or arm
- Severe pain
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a brachial plexus injury often involves a physical examination, during which the doctor may check for muscle weakness and feeling in the arm and hand. Imaging tests, such as MRI and CT scans, may also be used to help determine the location and extent of the damage.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for brachial plexus injuries depends on the severity of the injury. Some mild injuries may heal on their own, while others may require physical therapy, medication, or surgery. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be necessary.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for a brachial plexus injury depends on the severity and location of the injury, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Some patients may recover fully, while others may experience long-term complications, such as chronic pain and muscle weakness.
See also[edit]
