Herkinorin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
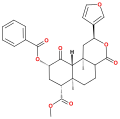
File:Herkinorin color.svg|Herkinorin | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:48, 16 March 2025
Herkinorin is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic that has been derived from the natural product Salvinorin A. It was discovered in 2005 by a team at Purdue University led by Richard B. Rothman and Kenner C. Rice. Herkinorin is the first compound found to be a full agonist for the peripheral μ-opioid receptor that does not significantly recruit β-arrestin-2 after binding to and activating the receptor.
Chemistry[edit]
Herkinorin is a semi-synthetic compound, which means it is not found in nature but is instead synthesized from natural products. It is derived from Salvinorin A, a psychoactive compound found in the plant Salvia divinorum. The chemical structure of Herkinorin is similar to that of other opioids, with a basic nitrogen atom and a phenolic hydroxyl group.
Pharmacology[edit]
Herkinorin acts as a full agonist at the μ-opioid receptor, but unlike most other μ-opioid receptor agonists, it does not significantly recruit β-arrestin-2. This is significant because the recruitment of β-arrestin-2 is associated with the development of opioid tolerance and dependence. Therefore, Herkinorin may have potential as a new type of opioid analgesic that is less likely to produce these side effects.
Research[edit]
Research on Herkinorin is still in the early stages, but initial studies suggest that it may have potential as a new type of opioid analgesic. Further research is needed to fully understand the pharmacology of Herkinorin and to determine its efficacy and safety in humans.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />