Estradiol/progesterone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
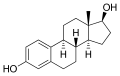
File:Estradiol.svg|Estradiol | |||
File:Progesterone.svg|Progesterone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 20:52, 16 March 2025
Estradiol/progesterone is a combination drug used in hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It contains two active ingredients: estradiol, a form of estrogen, and progesterone, a form of progestogen.
Pharmacology[edit]
Estradiol is a naturally occurring estrogen that is primarily responsible for the development and maintenance of female secondary sexual characteristics. It also plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Progesterone, on the other hand, is a naturally occurring progestogen that plays a vital role in maintaining pregnancy and regulating the menstrual cycle.
Clinical Use[edit]
Estradiol/progesterone is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, and vaginal dryness. It is also used in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to replace the declining levels of these hormones in the body during menopause.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all medications, estradiol/progesterone can cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, headache, breast tenderness, and mood changes. More serious side effects can include blood clots, stroke, and breast cancer.
Precautions[edit]
Before starting treatment with estradiol/progesterone, it is important to discuss your medical history with your healthcare provider. This medication should not be used in women with a history of breast cancer, uterine cancer, liver disease, or blood clots.
See Also[edit]
-
Estradiol
-
Progesterone