Myricanone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Myricanone.svg|Myricanone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:58, 3 March 2025
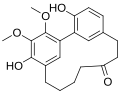
Myricanone is a chemical compound found in the bark of the Myrica cerifera (wax myrtle) tree. It is a member of the class of compounds known as flavonoids, which are widely distributed in the plant kingdom and are known for their diverse beneficial effects on human health.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Myricanone is a flavonoid with the chemical formula C30H18O10. Its structure consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C). The A ring is attached to the B ring at the 2 and 3 positions, and the C ring is attached to the A ring at the 1 and 2 positions. The B ring carries a hydroxyl group at the 4' position, and the A ring carries a carbonyl group at the 4 position.
Biological Activity[edit]
Myricanone has been found to exhibit several biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects. It has also been shown to inhibit the growth of certain types of cancer cells in laboratory studies.
Antioxidant Activity[edit]
Like many flavonoids, myricanone has potent antioxidant activity. It can scavenge free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and contribute to aging and diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Anti-inflammatory Activity[edit]
Myricanone has been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are substances that can trigger inflammation in the body. This suggests that it may have potential as a natural anti-inflammatory agent.
Antimicrobial Activity[edit]
Studies have shown that myricanone has antimicrobial activity against a range of bacteria and fungi. This includes Staphylococcus aureus, a common cause of skin infections, and Candida albicans, a fungus that can cause oral and genital infections.
Anticancer Activity[edit]
In laboratory studies, myricanone has been found to inhibit the growth of certain types of cancer cells, including breast and lung cancer cells. It appears to do this by inducing apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
Potential Therapeutic Uses[edit]
Given its biological activities, myricanone has potential for use in the treatment of a range of conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancer. However, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and to determine its safety and efficacy in humans.
-
Myricanone