Retapamulin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
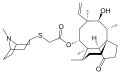
File:Retapamulin.svg|Retapamulin | |||
File:Retapamulin 3D sticks.png|Retapamulin 3D Sticks | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:24, 20 February 2025
Retapamulin is a topical antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections on the skin. It is a member of the pleuromutilin class of antibiotics and is primarily used to treat impetigo and other skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
History[edit]
Retapamulin was developed by GlaxoSmithKline and approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2007. It was the first pleuromutilin antibiotic to be approved for use in humans.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Retapamulin works by inhibiting the synthesis of protein in bacteria, which is necessary for their growth and reproduction. It binds to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, preventing the addition of new amino acids to the growing peptide chain.
Usage[edit]
Retapamulin is used topically, typically in the form of a 1% ointment. It is applied to the affected area twice a day for a period of five days. It is not recommended for use in patients under the age of 9 months.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of retapamulin include irritation at the site of application, headache, and nausea. In rare cases, it can cause severe allergic reactions.
Resistance[edit]
As with all antibiotics, there is a risk of bacteria developing resistance to retapamulin. However, due to its unique mechanism of action, cross-resistance with other classes of antibiotics is less likely.
See Also[edit]
-
Retapamulin
-
Retapamulin 3D Sticks