Electrode: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Arc_welding_electrodes_and_electrode_holder.triddle.jpg|Arc welding electrodes and electrode holder | |||
File:Galvanic_cell_with_no_cation_flow.svg|Galvanic cell with no cation flow | |||
File:Batteries.jpg|Batteries | |||
File:Rechargable_Batteries_(50826854891).jpg|Rechargeable batteries | |||
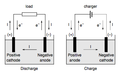
File:Fig_bat_Discharge_Charge3.png|Battery discharge and charge | |||
File:Hush_adiabatic_electron_transfer_model_parameters.png|Hush adiabatic electron transfer model parameters | |||
File:Redox_Flow_Battery.jpg|Redox flow battery | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 18 February 2025
Electrode is a conductor through which electricity enters or leaves an object, substance, or region. They are used in a wide range of applications, including but not limited to, electronics, chemistry, and medicine.
Overview[edit]
An Electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). The word was coined by William Whewell at the request of the scientist Michael Faraday from two Greek words: elektron, meaning amber (from which the word electricity is derived), and hodos, a way.
Types of Electrodes[edit]
There are two types of electrodes: Anode and Cathode. The anode is positively charged, while the cathode is negatively charged.
Anode[edit]
The Anode is the electrode where oxidation (loss of electrons) takes place. In a galvanic cell, it is the negative electrode, as it is the electrode that provides electrons. In an electrolytic cell, it is the positive electrode.
Cathode[edit]
The Cathode is the electrode where reduction (gain of electrons) takes place. In a galvanic cell, it is the positive electrode, as it is the electrode that accepts electrons. In an electrolytic cell, it is the negative electrode.
Electrodes in Medicine[edit]
In medicine, electrodes are used in numerous ways, including in ECG machines to monitor heart activity, in EEG machines to monitor brain activity, and in ECT for treating mental disorders.
See Also[edit]
- Electrolysis
- Electrochemical cell
- Battery
- Fuel cell
- Electrode potential
- Standard electrode potential
References[edit]
<references />