Neurolinguistics: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Neurolinguistics == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray726-Brodman.png|Brodmann areas of the brain | |||
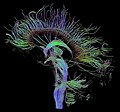
File:DTI-sagittal-fibers.jpg|Sagittal view of brain fibers using DTI | |||
File:Brain_-_Broca's_and_Wernicke's_area_Diagram.svg|Diagram of Broca's and Wernicke's areas | |||
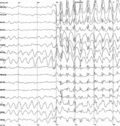
File:Spike-waves.png|Spike waves in EEG | |||
File:ComponentsofERP.svg|Components of an ERP | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:37, 18 February 2025
Neurolinguistics is an interdisciplinary field that combines the study of neuroscience and linguistics. It seeks to understand how the brain processes language and how language affects the brain. Neurolinguistics is a relatively new field, but it has already made significant contributions to our understanding of language and the brain.
History[edit]
The field of neurolinguistics began in the 19th century with the work of Paul Broca and Carl Wernicke. Broca discovered that damage to a specific area of the brain, now known as Broca's area, resulted in speech production difficulties. Wernicke found that damage to a different area, now known as Wernicke's area, resulted in comprehension difficulties. These discoveries laid the foundation for the field of neurolinguistics.
Research Methods[edit]
Neurolinguistics uses a variety of research methods to study the brain and language. These include neuroimaging techniques such as MRI and fMRI, which allow researchers to visualize the brain and see which areas are active during language tasks. Other methods include electroencephalography (EEG), which measures electrical activity in the brain, and lesion studies, which examine the effects of brain damage on language abilities.
Key Concepts[edit]
One of the key concepts in neurolinguistics is the idea of lateralization, or the idea that certain cognitive functions are primarily controlled by one hemisphere of the brain. In most right-handed individuals, for example, language processing is primarily controlled by the left hemisphere. Another key concept is modularity, or the idea that different aspects of language are processed in different areas of the brain.
Applications[edit]
Neurolinguistics has many practical applications. It can help us understand and treat language disorders, such as aphasia and dyslexia. It can also inform our understanding of how children learn language, and how language changes with age.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />