Pterygopalatine fossa: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
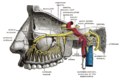
File:Gray159.png|Diagram showing the position of the pterygopalatine fossa. | |||
File:Pterygopalatine_fossa.PNG|Anatomical illustration of the pterygopalatine fossa. | |||
File:Gray779.png|Lateral view of the skull showing the pterygopalatine fossa. | |||
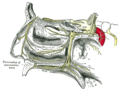
File:Gray780.png|Medial view of the skull with the pterygopalatine fossa highlighted. | |||
File:Pteryopalatinahd.jpg|High-definition image of the pterygopalatine fossa. | |||
File:Pterygopalatine_fossa.jpg|Photograph of the pterygopalatine fossa. | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:35, 18 February 2025
Pterygopalatine fossa
The Pterygopalatine fossa is a complex anatomical area located in the skull, specifically in the inferior part of the pterygoid process and the palatine bone. It is a bilateral, cone-shaped depression extending deep into the facial skeleton.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Pterygopalatine" is derived from the Greek words "pteryx" meaning wing and "palatum" meaning roof of the mouth. The term "fossa" is derived from the Latin word for ditch or trench.
Anatomy[edit]
The pterygopalatine fossa is bounded by the maxillary bone anteriorly, the sphenoid bone posteriorly, and the palatine bone inferiorly. It communicates with several other anatomical spaces, including the oral cavity, nasal cavity, orbit, and middle cranial fossa.
Clinical significance[edit]
Due to its location and the numerous structures it contains, the pterygopalatine fossa is clinically significant in several medical fields, including otolaryngology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and neurology. It is often involved in procedures such as maxillary nerve blocks and endoscopic sinus surgeries.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Diagram showing the position of the pterygopalatine fossa.
-
Anatomical illustration of the pterygopalatine fossa.
-
Lateral view of the skull showing the pterygopalatine fossa.
-
Medial view of the skull with the pterygopalatine fossa highlighted.
-
High-definition image of the pterygopalatine fossa.
-
Photograph of the pterygopalatine fossa.