Mallory body: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Mallory_body_high_mag_cropped.jpg|Mallory body high magnification cropped | |||
File:Mallory_body_high_mag.jpg|Mallory body high magnification | |||
File:Mallory_body_intermed_mag.jpg|Mallory body intermediate magnification | |||
File:CDC_mallory_bodies.jpg|CDC Mallory bodies | |||
File:Hepatocellular_carcinoma_intermed_mag.jpg|Hepatocellular carcinoma intermediate magnification | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:32, 18 February 2025
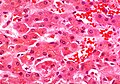
Mallory body is a type of intracellular inclusion found in the liver cells of individuals with certain types of liver disease. It was first described by Frank Burr Mallory in 1911.
Overview[edit]
Mallory bodies are intracellular inclusions that are found in the liver cells of individuals with certain types of liver disease. They are named after Frank Burr Mallory, an American pathologist who first described them in 1911. Mallory bodies are composed of tangled aggregates of intermediate filaments and other proteins, and their presence in liver cells is a marker of cellular injury.
Composition[edit]
Mallory bodies are composed of tangled aggregates of intermediate filaments, which are a type of protein structure found in the cells of many types of tissues. In addition to intermediate filaments, Mallory bodies also contain other proteins, including ubiquitin, a protein that is involved in the degradation of damaged or unneeded proteins in cells.
Associated Conditions[edit]
The presence of Mallory bodies in liver cells is associated with a number of different conditions, including alcoholic hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer. They are also found in some cases of Wilson's disease, a genetic disorder that causes copper to accumulate in the liver, and primary biliary cirrhosis, a disease in which the bile ducts in the liver are slowly destroyed.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The presence of Mallory bodies in liver cells is a marker of cellular injury. They are often found in liver cells that have been damaged by alcohol or other toxins. However, the exact role that Mallory bodies play in the development and progression of liver disease is not fully understood.