Breast reconstruction: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
{{Surgery-stub}} | {{Surgery-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Breast_reconstruction_2.jpg|Breast reconstruction | |||
File:Blausen_0138_BreastReconstruction_Expander.png|Breast reconstruction expander | |||
File:Blausen_0139_BreastReconstruction_Prosthesis.png|Breast reconstruction prosthesis | |||
File:Blausen_0140_BreastReconstruction_TRAM.png|Breast reconstruction TRAM | |||
File:Blausen_0141_BreastReconstruction_TRAM_PostOp.png|Breast reconstruction TRAM post-op | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:30, 18 February 2025
Breast Reconstruction is a surgical procedure that restores the shape, appearance, symmetry, and size of the breast following mastectomy, lumpectomy or other traumas. This procedure can be performed either immediately following the breast removal surgery, or it can be delayed until a later date.
Types of Breast Reconstruction[edit]
There are two primary types of breast reconstruction: implant-based reconstruction and autologous reconstruction.
Implant-based Reconstruction[edit]
In implant-based reconstruction, a breast implant is used to form a new breast mound. Implant-based reconstruction can be done in one stage, known as direct-to-implant reconstruction, or in two stages involving the use of a tissue expander.
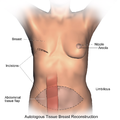
Autologous Reconstruction[edit]
In autologous reconstruction, tissue from another part of the patient's body, such as the abdomen, back, buttocks, or thigh, is used to form a new breast mound. There are several types of autologous reconstruction, including TRAM flap, DIEP flap, latissimus dorsi flap, and SGAP/IGAP flap.
Considerations for Breast Reconstruction[edit]
Several factors can influence the decision to undergo breast reconstruction, the type of reconstruction, and the timing of the surgery. These factors include the patient's overall health, stage of breast cancer, size of the natural breast, amount of available tissue for autologous reconstruction, desire for bilateral breast surgery, and personal preference.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any surgery, breast reconstruction carries potential risks and complications. These may include infection, bleeding, anesthesia risks, poor healing, implant rupture, and dissatisfaction with cosmetic results.
Recovery and Aftercare[edit]
Recovery from breast reconstruction surgery varies depending on the individual and the type of reconstruction performed. Post-operative care may include pain management, wound care, and physical therapy exercises to restore range of motion and strength.
See Also[edit]