Histone deacetylase: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[Category:Gene expression]] | [[Category:Gene expression]] | ||
[[Category:Epigenetics]] | [[Category:Epigenetics]] | ||
== Histone deacetylase == | |||
<gallery> | |||
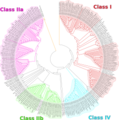
File:Figure1_tree.tif|Phylogenetic tree of histone deacetylases | |||
File:Histone_tails_set_for_transcriptional_activation.jpg|Histone tails set for transcriptional activation | |||
File:Histone_tails_set_for_transcriptional_repression.jpg|Histone tails set for transcriptional repression | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:12, 18 February 2025
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) is a type of enzyme that plays a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression. HDACs are part of a larger family of proteins that are involved in the modification of histones, the proteins around which DNA is wound to form chromosomes.
Function[edit]
HDACs remove acetyl groups from the histones, which leads to the condensation of the DNA-histone complex and the suppression of gene expression. This process is known as histone deacetylation.
Types[edit]
There are four classes of HDACs:
- Class I includes HDACs 1, 2, 3, and 8. These are found in the nucleus and are involved in cell survival and proliferation.
- Class II includes HDACs 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10. These can shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and are involved in a variety of cellular processes.
- Class III includes the sirtuins, which are involved in aging and metabolism.
- Class IV includes only HDAC11, which has properties of both Class I and II HDACs.
Role in Disease[edit]
Abnormal HDAC activity has been linked to a number of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. In cancer, for example, increased HDAC activity can lead to the silencing of tumor suppressor genes.
HDAC Inhibitors[edit]
HDAC inhibitors are a class of drugs that block the activity of HDACs. They are being investigated for their potential to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.