Nefopam: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
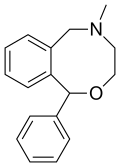
File:Nefopam2DACS.svg|2D structure of Nefopam | |||
File:Nefopam_ball-and-stick_model.png|Ball-and-stick model of Nefopam | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 17 February 2025
Nefopam is a non-opioid, non-steroidal, centrally acting analgesic drug that is used for the relief of moderate to severe pain. It is most commonly used in Europe, although it is also available in other parts of the world. The exact mechanism of action is not known, but it is thought to work by blocking the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain.
Pharmacology[edit]
Nefopam is a non-opioid analgesic that is not structurally related to other non-opioid analgesics. It is thought to work by blocking the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain, which helps to reduce pain. Nefopam does not have any anti-inflammatory properties, and it does not interact with opioid receptors.
Uses[edit]
Nefopam is used for the relief of moderate to severe pain. It can be used alone or in combination with other analgesics. It is also used for the prevention of pain after surgery.
Side effects[edit]
The most common side effects of nefopam include nausea, vomiting, sweating, and dizziness. Less common side effects include dry mouth, tachycardia, confusion, and hallucinations.
Contraindications[edit]
Nefopam should not be used in people with a history of seizures, as it can increase the risk of seizures. It should also not be used in people with a history of psychosis, as it can exacerbate the symptoms.
Interactions[edit]
Nefopam can interact with other medications, including other analgesics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. It can also interact with alcohol, increasing the risk of side effects.