Human overpopulation: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Article about the concept of human overpopulation}} | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
{{Globalize|date=October 2023}} | |||
[[File:UN_population_estimates_and_projection_1950-2011.png|thumb|right|300px|UN population estimates and projections from 1950 to 2011.]] | |||
[[File:Total_Fertility_Rate_Map_by_Country.svg|thumb|right|300px|Map showing total fertility rate by country.]] | |||
'''Human overpopulation''' refers to a condition where the number of humans exceeds the carrying capacity of the Earth. This concept is often discussed in terms of the environmental, social, and economic impacts of a growing human population. | |||
==Overview== | |||
Human overpopulation is a complex issue that involves the interplay of various factors such as [[fertility rate]], [[mortality rate]], and [[migration]]. The [[United Nations]] has projected that the global population could reach 9.7 billion by 2050, which raises concerns about the sustainability of resources and the environment. | |||
=== | ===Historical Context=== | ||
The concept of overpopulation has been a topic of concern since the publication of [[Thomas Malthus]]'s "An Essay on the Principle of Population" in 1798. Malthus argued that population growth would outpace agricultural production, leading to widespread famine and poverty. While technological advancements have delayed such outcomes, the rapid increase in population continues to pose significant challenges. | |||
===Causes=== | |||
Several factors contribute to human overpopulation: | |||
* '''High Birth Rates''': In many developing countries, high birth rates contribute significantly to population growth. Cultural, religious, and economic factors often encourage large families. | |||
* '''Decreased Mortality Rates''': Advances in medicine and public health have significantly reduced mortality rates, leading to longer life expectancies and increased population. | |||
* '''Migration''': Migration can lead to overpopulation in certain areas, especially urban centers, as people move in search of better opportunities. | |||
===Impacts=== | |||
The impacts of human overpopulation are wide-ranging and include: | |||
=== | * '''Environmental Degradation''': Overpopulation leads to increased demand for resources, resulting in deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and pollution. | ||
* [[ | * '''Economic Strain''': High population density can strain infrastructure, healthcare, and education systems, leading to economic challenges. | ||
* '''Social Issues''': Overpopulation can exacerbate social issues such as poverty, unemployment, and inadequate housing. | |||
==Solutions== | |||
Addressing human overpopulation requires a multifaceted approach: | |||
* '''Family Planning''': Promoting family planning and access to contraceptives can help control birth rates. | |||
* '''Education''': Educating women and girls is one of the most effective ways to reduce fertility rates and improve economic outcomes. | |||
* '''Sustainable Development''': Implementing sustainable development practices can help balance population growth with resource availability. | |||
==Also see== | |||
* [[Carrying capacity]] | |||
* [[Demographic transition]] | |||
* [[Sustainable development]] | * [[Sustainable development]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Population density]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Environmental impact of agriculture]] | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category: | ==External links== | ||
* [https://www.un.org/en/sections/issues-depth/population/index.html United Nations Population Division] | |||
* [https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/population World Bank Population Overview] | |||
[[Category:Human population]] | |||
[[Category:Environmental issues]] | [[Category:Environmental issues]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Sociology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 10 December 2024
Article about the concept of human overpopulation
The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (October 2023) |

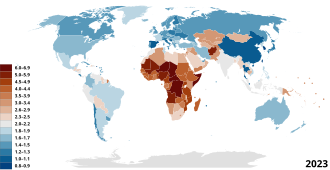
Human overpopulation refers to a condition where the number of humans exceeds the carrying capacity of the Earth. This concept is often discussed in terms of the environmental, social, and economic impacts of a growing human population.
Overview[edit]
Human overpopulation is a complex issue that involves the interplay of various factors such as fertility rate, mortality rate, and migration. The United Nations has projected that the global population could reach 9.7 billion by 2050, which raises concerns about the sustainability of resources and the environment.
Historical Context[edit]
The concept of overpopulation has been a topic of concern since the publication of Thomas Malthus's "An Essay on the Principle of Population" in 1798. Malthus argued that population growth would outpace agricultural production, leading to widespread famine and poverty. While technological advancements have delayed such outcomes, the rapid increase in population continues to pose significant challenges.
Causes[edit]
Several factors contribute to human overpopulation:
- High Birth Rates: In many developing countries, high birth rates contribute significantly to population growth. Cultural, religious, and economic factors often encourage large families.
- Decreased Mortality Rates: Advances in medicine and public health have significantly reduced mortality rates, leading to longer life expectancies and increased population.
- Migration: Migration can lead to overpopulation in certain areas, especially urban centers, as people move in search of better opportunities.
Impacts[edit]
The impacts of human overpopulation are wide-ranging and include:
- Environmental Degradation: Overpopulation leads to increased demand for resources, resulting in deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and pollution.
- Economic Strain: High population density can strain infrastructure, healthcare, and education systems, leading to economic challenges.
- Social Issues: Overpopulation can exacerbate social issues such as poverty, unemployment, and inadequate housing.
Solutions[edit]
Addressing human overpopulation requires a multifaceted approach:
- Family Planning: Promoting family planning and access to contraceptives can help control birth rates.
- Education: Educating women and girls is one of the most effective ways to reduce fertility rates and improve economic outcomes.
- Sustainable Development: Implementing sustainable development practices can help balance population growth with resource availability.
Also see[edit]
- Carrying capacity
- Demographic transition
- Sustainable development
- Population density
- Environmental impact of agriculture
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>