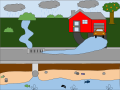
Surface runoff
Surface runoff is the flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater, or other sources flows over the Earth's surface. This might occur because soil is saturated to full capacity, because rain arrives more quickly than soil can absorb it, or because impervious areas (roofs and pavement) send their runoff to surrounding soil that cannot absorb all of it.
Overview
Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent of soil erosion by water. The land area producing runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. When runoff flows along the ground, it can pick up soil contaminants such as petroleum, pesticides, or fertilizers that become discharge or nonpoint source pollution.
Factors influencing runoff
Several factors affect the amount of surface runoff from a drainage basin, including rainfall, soil type, vegetation, and the slope of the land.
Rainfall
The amount and intensity of rainfall are the primary factors that determine the amount of surface runoff. The greater the intensity and duration of the rainfall, the greater the amount of runoff.
Soil type
Different types of soil have different infiltration rates. Clay soils have a low infiltration rate and produce more surface runoff than sandy soils, which have high infiltration rates.
Vegetation
Vegetation can affect surface runoff by intercepting rain and allowing more time for it to infiltrate the soil. Vegetation can also create a physical barrier, slowing the flow of runoff and allowing more time for it to infiltrate.
Slope of the land
The slope of the land can greatly affect the amount of surface runoff. Steeper slopes are more likely to result in runoff because water will flow downhill rather than infiltrating the soil.
Effects of surface runoff
Surface runoff can have several effects on the environment, both positive and negative. It can lead to soil erosion, which can result in the loss of fertile topsoil and the alteration of habitats. It can also lead to water pollution if it picks up pollutants from the ground surface.
See also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD