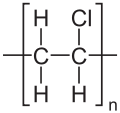
Polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic plastic polymer, after polyethylene and polypropylene. About 40 million tonnes are produced per year.
History[edit]
PVC was synthesized in 1872 by German chemist Eugen Baumann after extended investigation and experimentation. The polymer appeared as a white solid inside a flask of vinyl chloride that had been left exposed to sunlight. In the early 20th century the Russian chemist Ivan Ostromislensky and Fritz Klatte of the German chemical company Griesheim-Elektron both attempted to use PVC in commercial products, but difficulties in processing the rigid, sometimes brittle polymer thwarted their efforts.
Production[edit]
PVC is produced by polymerization of the vinyl chloride monomer (VCM). Suspension polymerization affords particles with average diameters of 100–180 μm, whereas emulsion polymerization gives much smaller particles of average size around 0.2 μm. VCM and water are introduced into the reactor along with a polymerization initiator and other additives. The contents of the reaction vessel are pressurized and continually mixed to maintain the suspension and ensure a uniform particle size of the PVC resin. The reaction is exothermic and thus requires cooling.
Properties[edit]
PVC comes in two basic forms: rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible. The rigid form of PVC is used in construction for pipe and in profile applications such as doors and windows. It is also used for bottles, other non-food packaging, and cards (such as bank or membership cards). It can be made softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers, the most widely used being phthalates. In this form, it is also used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, flooring, signage, phonograph records, inflatable products, and many applications where it replaces rubber.
Health and safety[edit]
In the EU the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) lists 2 phthalates (DBP and BBP), 2 groups of phthalates (DEHP, DIBP, BBP and DBP) and HBCDD in the Candidate List of substances of very high concern for their effects on human health.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian