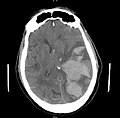
Brain herniation
Brain herniation is a potentially fatal condition that occurs when parts of the brain are displaced from their usual position due to increased intracranial pressure. This displacement can compress brain structures and blood vessels, leading to decreased blood flow, oxygen deprivation, and further increase in intracranial pressure, creating a vicious cycle. Brain herniation can result from various causes, including traumatic brain injury, stroke, tumors, and infections.
Types
There are several types of brain herniation, each with distinct characteristics and implications for treatment and prognosis:
- Uncal herniation: This occurs when the uncus of the temporal lobe shifts downward, potentially compressing the brainstem and the third cranial nerve.
- Central herniation: In this type, the diencephalon and parts of the temporal lobes shift downward through the tentorial notch.
- Cingulate herniation: This involves the displacement of the cingulate gyrus under the falx cerebri.
- Transcalvarial herniation: Brain tissue herniates through a defect in the skull, often due to surgery or trauma.
- Tonsillar herniation: Also known as cerebellar or foramen magnum herniation, this occurs when the cerebellar tonsils move downward through the foramen magnum, potentially compressing the brainstem and leading to death.
Symptoms
Symptoms of brain herniation can vary depending on the type but may include:
- Changes in consciousness, ranging from drowsiness to coma
- Pupil dilation, particularly on one side, if the third cranial nerve is affected
- Changes in breathing patterns
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
- Headache
- Seizures
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of brain herniation involves clinical assessment and imaging studies. Computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are crucial for identifying the type and extent of herniation.
Treatment
Treatment of brain herniation is a medical emergency and focuses on reducing intracranial pressure, treating the underlying cause, and supporting vital functions. Interventions may include:
- Medications to reduce brain swelling, such as mannitol or hypertonic saline
- Ventriculostomy to drain cerebrospinal fluid and relieve pressure
- Surgical decompression to remove the source of increased pressure or to create more space for the swollen brain
Prognosis
The prognosis for brain herniation depends on the speed of diagnosis and treatment, the underlying cause, and the extent of brain damage. Early intervention can improve outcomes, but the condition can be fatal without prompt treatment.
Prevention
Preventing brain herniation involves managing conditions that can lead to increased intracranial pressure, such as head injuries, strokes, and brain tumors, with appropriate medical and surgical interventions.
-
Decorticate posturing
-
Types of brain herniation
-
Subfalcine herniation
-
Brain injury with herniation on MRI
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian