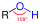
Everclear
Everclear is a brand of neutral grain spirit that is bottled at two high proofs: 151 (75.5% alcohol by volume) and 190 (95% alcohol by volume). Produced in the United States by Luxco (formerly known as the David Sherman Corporation), Everclear is made from corn and is marketed as an unaged spirit. Due to its high alcohol content, Everclear is considered extremely potent and should be handled with care.
History
Everclear was introduced by Luxco in the 1950s. The product's development was part of a trend towards higher-proof beverages, driven by both consumer demand and the practical benefits of shipping higher concentrations of alcohol. Over the years, Everclear has gained a reputation for its extreme potency and has been subject to various regulations and bans in different jurisdictions.
Production
Everclear is produced through a process of fermentation and distillation. The corn is first fermented, converting its sugars into alcohol. This alcohol is then distilled to increase its purity and alcohol content. The final product is a clear, colorless spirit with a neutral taste, making it a versatile base for a wide range of cocktails and homemade liqueurs.
Regulations
Due to its high alcohol content, the sale of Everclear is heavily regulated or banned in some areas. For example, the 190-proof version is illegal in several U.S. states due to concerns about alcohol abuse and potential health risks. Consumers are advised to check local laws before purchasing or using Everclear.
Health Risks
The consumption of high-proof spirits like Everclear poses significant health risks. These include alcohol poisoning, increased risk of accidents, and long-term health issues such as liver damage. It is crucial to consume Everclear in moderation, if at all, and to be aware of its potent effects.
Uses
While Everclear is often associated with high-risk drinking practices, it also has legitimate uses in the culinary and scientific fields. In the kitchen, it can be used to extract flavors for homemade extracts and tinctures or as a base for liqueurs. In the laboratory, Everclear serves as a solvent or cleaning agent due to its high purity and alcohol content.
Controversy
Everclear has been at the center of controversy due to its association with dangerous drinking behaviors, including binge drinking and alcohol poisoning. Critics argue that its high alcohol content makes it too risky for consumption, while supporters claim that responsible use is possible and that Everclear offers benefits in culinary and scientific applications.
Conclusion
Everclear is a highly potent spirit that requires careful handling and responsible consumption. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in certain applications, but its potential for abuse and health risks cannot be ignored. Consumers should be fully informed about the effects of high-proof alcohol and adhere to local regulations regarding its purchase and use.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian