Magnesium trisilicate
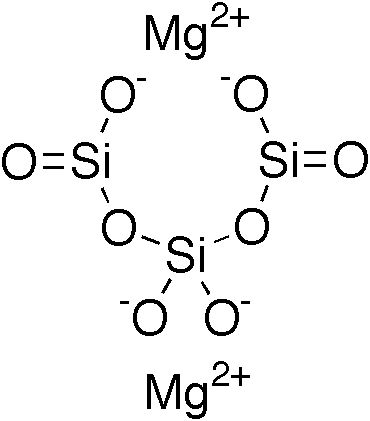
Magnesium trisilicate is an inorganic compound composed of magnesium, silicon, and oxygen with the chemical formula Mg_2Si_3O_8. It is used primarily as an antacid and in the pharmaceutical industry as an excipient to control the acidity of certain pharmaceutical products. Magnesium trisilicate can neutralize stomach acid by reacting with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form magnesium chloride (MgCl_2), silicon dioxide (SiO_2), and water (H_2O).
Properties
Magnesium trisilicate is a white, odorless powder that is insoluble in water but can react with acids. This reaction is what makes it effective as an antacid. The compound's ability to neutralize stomach acid without causing a significant change in the stomach's overall pH makes it a gentle option for treating symptoms of heartburn, acid reflux, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Uses
The primary use of magnesium trisilicate is as an antacid in the treatment of conditions related to excess stomach acid. It is often combined with other antacids to enhance its effectiveness. In addition to its use in treating digestive issues, magnesium trisilicate is also used in the pharmaceutical industry as an excipient. An excipient is an inactive substance that serves as the vehicle or medium for a drug or other active substances. In this role, magnesium trisilicate helps to control the acidity of pharmaceutical products, ensuring their stability and efficacy.
Safety and Side Effects
While magnesium trisilicate is generally considered safe for most individuals, there are potential side effects and interactions to be aware of. Excessive use can lead to magnesium toxicity, which can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It can also interact with certain medications, affecting their absorption and efficacy. Therefore, it is important to use magnesium trisilicate under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with kidney disease or those taking other medications.
Regulation
In many countries, magnesium trisilicate and products containing it are regulated by health authorities such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. These regulations ensure that products are safe for consumption and are manufactured according to specific quality standards.
Conclusion
Magnesium trisilicate is a valuable compound in both the medical and pharmaceutical fields due to its antacid properties and role as an excipient. Its ability to neutralize stomach acid gently and effectively makes it a common ingredient in over-the-counter antacid medications. However, like all medications, it is important to use magnesium trisilicate responsibly to avoid potential side effects and interactions.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
