Hibernoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hibernoma | |||
| image = [[File:Hibernoma1.jpg]] | |||
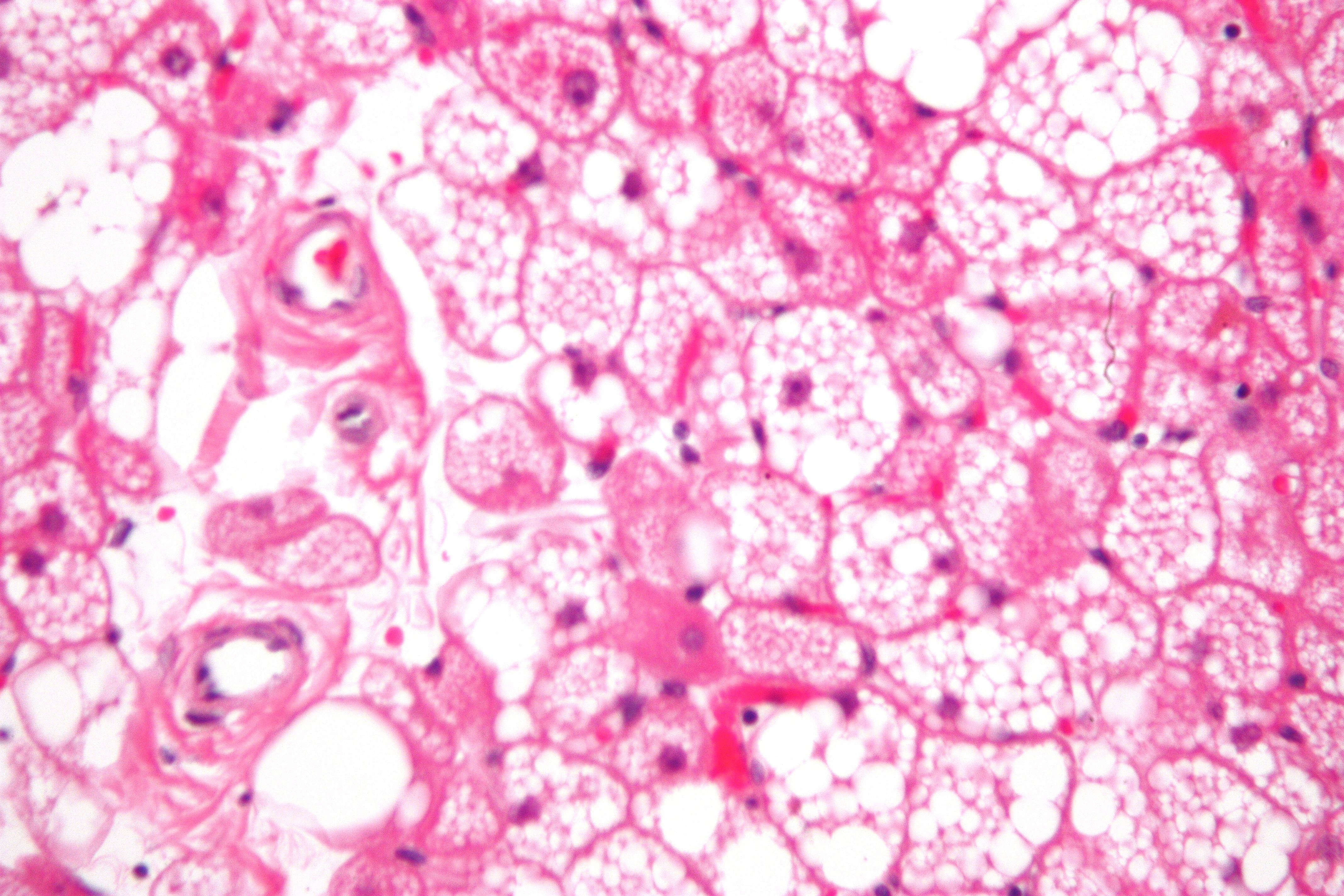
| caption = Histopathological image of a hibernoma | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = Usually asymptomatic, may present as a painless mass | |||
| complications = Rarely, compression of adjacent structures | |||
| onset = Typically in adults | |||
| duration = Indefinite | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = [[Histopathology]], [[Imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Liposarcoma]], [[Lipoma]], [[Myxoid liposarcoma]] | |||
| prevention = None | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical excision]] | |||
| medication = None | |||
| prognosis = Excellent with complete excision | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Hibernoma2.jpg|Hibernoma|left|thumb]] | |||
'''Hibernoma''' is a rare, benign [[tumor]] that originates from brown [[fat tissue]]. The name "hibernoma" is derived from the tumor's resemblance to the brown fat found in hibernating animals. | '''Hibernoma''' is a rare, benign [[tumor]] that originates from brown [[fat tissue]]. The name "hibernoma" is derived from the tumor's resemblance to the brown fat found in hibernating animals. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
The first known case of hibernoma was reported by Merkel in 1906. Since then, fewer than 200 cases have been reported in the medical literature. | The first known case of hibernoma was reported by Merkel in 1906. Since then, fewer than 200 cases have been reported in the medical literature. | ||
== Pathology == | == Pathology == | ||
Hibernomas are composed of brown fat cells, which are larger than white fat cells and contain more [[mitochondria]]. These cells are responsible for heat production in the body, a process known as [[thermogenesis]]. | Hibernomas are composed of brown fat cells, which are larger than white fat cells and contain more [[mitochondria]]. These cells are responsible for heat production in the body, a process known as [[thermogenesis]]. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Patients with hibernoma often present with a slow-growing, painless mass. The most common locations for hibernomas are the thigh, shoulder, back, and neck. | Patients with hibernoma often present with a slow-growing, painless mass. The most common locations for hibernomas are the thigh, shoulder, back, and neck. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of hibernoma is typically made through a combination of [[imaging studies]] and [[biopsy]]. On imaging, hibernomas appear as well-defined, vascular masses. The definitive diagnosis is made by biopsy, which shows the characteristic brown fat cells. | The diagnosis of hibernoma is typically made through a combination of [[imaging studies]] and [[biopsy]]. On imaging, hibernomas appear as well-defined, vascular masses. The definitive diagnosis is made by biopsy, which shows the characteristic brown fat cells. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment for hibernoma is surgical removal. Because hibernomas are benign, they do not spread to other parts of the body, and complete removal is usually curative. | The treatment for hibernoma is surgical removal. Because hibernomas are benign, they do not spread to other parts of the body, and complete removal is usually curative. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for patients with hibernoma is excellent. After surgical removal, the recurrence rate is very low. | The prognosis for patients with hibernoma is excellent. After surgical removal, the recurrence rate is very low. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Lipoma]] | * [[Lipoma]] | ||
* [[Liposarcoma]] | * [[Liposarcoma]] | ||
* [[Benign tumors]] | * [[Benign tumors]] | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Tumors]] | [[Category:Tumors]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hibernoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Usually asymptomatic, may present as a painless mass |
| Complications | Rarely, compression of adjacent structures |
| Onset | Typically in adults |
| Duration | Indefinite |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, Imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Liposarcoma, Lipoma, Myxoid liposarcoma |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Surgical excision |
| Medication | None |
| Prognosis | Excellent with complete excision |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Hibernoma is a rare, benign tumor that originates from brown fat tissue. The name "hibernoma" is derived from the tumor's resemblance to the brown fat found in hibernating animals.
History[edit]
The first known case of hibernoma was reported by Merkel in 1906. Since then, fewer than 200 cases have been reported in the medical literature.
Pathology[edit]
Hibernomas are composed of brown fat cells, which are larger than white fat cells and contain more mitochondria. These cells are responsible for heat production in the body, a process known as thermogenesis.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with hibernoma often present with a slow-growing, painless mass. The most common locations for hibernomas are the thigh, shoulder, back, and neck.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of hibernoma is typically made through a combination of imaging studies and biopsy. On imaging, hibernomas appear as well-defined, vascular masses. The definitive diagnosis is made by biopsy, which shows the characteristic brown fat cells.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for hibernoma is surgical removal. Because hibernomas are benign, they do not spread to other parts of the body, and complete removal is usually curative.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with hibernoma is excellent. After surgical removal, the recurrence rate is very low.


