Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | |||
| image = [[File:Dermatofibrosarcoma_protuberans_(1)_recurrence.JPG|250px]] | |||
| caption = Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans on the skin | |||
| field = [[Dermatology]], [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = DFSP | |||
| symptoms = Slow-growing skin nodule, often on the trunk or limbs | |||
| complications = Local recurrence, rarely metastasis | |||
| onset = Typically between 20 and 50 years of age | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] involving [[chromosome 17]] and [[chromosome 22]] | |||
| risks = Previous trauma to the skin, [[genetic predisposition]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Biopsy]], [[Histopathology]] | |||
| differential = [[Dermatofibroma]], [[Keloid]], [[Lipoma]], [[Melanoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical excision]], [[Mohs micrographic surgery]], [[Radiation therapy]] | |||
| medication = [[Imatinib]] for unresectable or metastatic cases | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with complete excision | |||
| frequency = 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 1,000,000 per year | |||
| deaths = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Other Names:''' | '''Other Names:''' | ||
DFSP; Giant cell fibroblastoma; Familial dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype); Metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype) | DFSP; Giant cell fibroblastoma; Familial dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype); Metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype) | ||
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is an uncommon cancer in which [[tumors]] arise in the deeper layers of skin. The tumor usually starts as a small, firm patch of skin; it may be purplish, reddish, or flesh-colored. It is commonly found on the [[torso]], usually in the shoulder and chest area. | Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is an uncommon cancer in which [[tumors]] arise in the deeper layers of skin. The tumor usually starts as a small, firm patch of skin; it may be purplish, reddish, or flesh-colored. It is commonly found on the [[torso]], usually in the shoulder and chest area. | ||
The tumor typically grows slowly but has a tendency to recur after being removed. It rarely spreads to other parts of the body. | The tumor typically grows slowly but has a tendency to recur after being removed. It rarely spreads to other parts of the body. | ||
These tumors are related to giant cell fibroblastomas. | These tumors are related to giant cell fibroblastomas. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 16: | Line 35: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== '''Cause''' == | == '''Cause''' == | ||
The cause of DFSP is unknown but an injury to the affected skin may be a predisposing factor.[[Trauma]] at the affected site has been reported in approximately 10-20% of patients. | The cause of DFSP is unknown but an injury to the affected skin may be a predisposing factor.[[Trauma]] at the affected site has been reported in approximately 10-20% of patients. | ||
== '''Genetics and inheritance''' == | == '''Genetics and inheritance''' == | ||
Recent advances have shown that in approximately 90% of cases, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is associated with a rearrangement ([[translocation]]) of genetic material between [[chromosomes 17]] and 22 which results in the [[fusion]] of two genes. | Recent advances have shown that in approximately 90% of cases, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is associated with a rearrangement ([[translocation]]) of genetic material between [[chromosomes 17]] and 22 which results in the [[fusion]] of two genes. | ||
The [[fused gene]] produces a [[protein]] which some believe may stimulate cells to multiply, leading to the [[tumor]] formation seen in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. | The [[fused gene]] produces a [[protein]] which some believe may stimulate cells to multiply, leading to the [[tumor]] formation seen in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. | ||
This type of gene change is generally found only in tumor cells and is '''not inherited'''. | This type of gene change is generally found only in tumor cells and is '''not inherited'''. | ||
== '''Symptoms''' == | == '''Symptoms''' == | ||
or most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. | or most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 49: | ||
* Subcutaneous nodule(Firm lump under the skin) | * Subcutaneous nodule(Firm lump under the skin) | ||
* Thickened skin(Thick skin) | * Thickened skin(Thick skin) | ||
30%-79% of people have these symptoms | 30%-79% of people have these symptoms | ||
* Skin ulcer(Open skin sore) | * Skin ulcer(Open skin sore) | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
DFSP is a [[malignant tumor]] diagnosed with a [[biopsy]], when a portion of the tumor is removed for examination. In order to ensure that enough tissue is removed to make an accurate diagnosis, the initial biopsy of a suspected DFSP is usually done with a core needle or a surgical incision. | DFSP is a [[malignant tumor]] diagnosed with a [[biopsy]], when a portion of the tumor is removed for examination. In order to ensure that enough tissue is removed to make an accurate diagnosis, the initial biopsy of a suspected DFSP is usually done with a core needle or a surgical incision. | ||
[[Magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) is more sensitive addressing the depth of the invasion on some types of DFSP, particularly large or recurring tumors. | [[Magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) is more sensitive addressing the depth of the invasion on some types of DFSP, particularly large or recurring tumors. | ||
== '''Treatment''' == | == '''Treatment''' == | ||
Treatment is primarily [[surgical]](Mohs surgery), with [[chemotherapy]] and [[radiation therapy]] used if clear margins are not acquired. | Treatment is primarily [[surgical]](Mohs surgery), with [[chemotherapy]] and [[radiation therapy]] used if clear margins are not acquired. | ||
The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition. | The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition. | ||
* '''[[Imatinib mesylate]]''' (Brand name: | * '''[[Imatinib mesylate]]''' (Brand name: Gleevec®)Treatment of adult patients with unresectable, recurrent and/or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) | ||
== '''Prognosis''' == | == '''Prognosis''' == | ||
Regular follow-up is needed after tumor removal to monitor for recurrence. | Regular follow-up is needed after tumor removal to monitor for recurrence. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 63: | ||
A small subset of patients with DFSP have a more aggressive variant known as [[fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans]] or FS-DFSP. | A small subset of patients with DFSP have a more aggressive variant known as [[fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans]] or FS-DFSP. | ||
FS-DFSP tumors are more likely to [[metastasize]] than the [[tumors]] in other types of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. | FS-DFSP tumors are more likely to [[metastasize]] than the [[tumors]] in other types of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. | ||
==Additional images== | ==Additional images== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 71: | ||
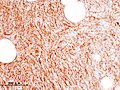
File:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (5) CD34.JPG|[[Immunostaining|Immunostain]] positive for [[CD34]] | File:Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (5) CD34.JPG|[[Immunostaining|Immunostain]] positive for [[CD34]] | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas}} | {{Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas}} | ||
{{Skin tumors, dermis}} | {{Skin tumors, dermis}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:18, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | DFSP |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Slow-growing skin nodule, often on the trunk or limbs |
| Complications | Local recurrence, rarely metastasis |
| Onset | Typically between 20 and 50 years of age |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation involving chromosome 17 and chromosome 22 |
| Risks | Previous trauma to the skin, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Biopsy, Histopathology |
| Differential diagnosis | Dermatofibroma, Keloid, Lipoma, Melanoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, Radiation therapy |
| Medication | Imatinib for unresectable or metastatic cases |
| Prognosis | Generally good with complete excision |
| Frequency | 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 1,000,000 per year |
| Deaths | Rare |
Other Names:
DFSP; Giant cell fibroblastoma; Familial dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype); Metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (subtype)
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is an uncommon cancer in which tumors arise in the deeper layers of skin. The tumor usually starts as a small, firm patch of skin; it may be purplish, reddish, or flesh-colored. It is commonly found on the torso, usually in the shoulder and chest area.
The tumor typically grows slowly but has a tendency to recur after being removed. It rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
These tumors are related to giant cell fibroblastomas.
Cause[edit]
The cause of DFSP is unknown but an injury to the affected skin may be a predisposing factor.Trauma at the affected site has been reported in approximately 10-20% of patients.
Genetics and inheritance[edit]
Recent advances have shown that in approximately 90% of cases, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is associated with a rearrangement (translocation) of genetic material between chromosomes 17 and 22 which results in the fusion of two genes. The fused gene produces a protein which some believe may stimulate cells to multiply, leading to the tumor formation seen in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. This type of gene change is generally found only in tumor cells and is not inherited.
Symptoms[edit]
or most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. 80%-99% of people have these symptoms
- Erythema
- Fibrosarcoma
- Neoplasm of the skin(Skin tumors)
- Subcutaneous nodule(Firm lump under the skin)
- Thickened skin(Thick skin)
30%-79% of people have these symptoms
- Skin ulcer(Open skin sore)
Diagnosis[edit]
DFSP is a malignant tumor diagnosed with a biopsy, when a portion of the tumor is removed for examination. In order to ensure that enough tissue is removed to make an accurate diagnosis, the initial biopsy of a suspected DFSP is usually done with a core needle or a surgical incision. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is more sensitive addressing the depth of the invasion on some types of DFSP, particularly large or recurring tumors.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment is primarily surgical(Mohs surgery), with chemotherapy and radiation therapy used if clear margins are not acquired. The medication(s) listed below have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as orphan products for treatment of this condition.
- Imatinib mesylate (Brand name: Gleevec®)Treatment of adult patients with unresectable, recurrent and/or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
Prognosis[edit]
Regular follow-up is needed after tumor removal to monitor for recurrence. Local recurrences arise in 11-20% of cases, usually within three years of the initial surgery. Despite being locally aggressive, the tumor spreads to other parts of the body (metastasizes) in only 5% of cases. A small subset of patients with DFSP have a more aggressive variant known as fibrosarcomatous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans or FS-DFSP. FS-DFSP tumors are more likely to metastasize than the tumors in other types of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.
Additional images[edit]
-
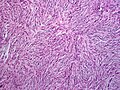
Subcutaneous tissue infiltration (i.e. "honeycomb" growth pattern)
-
Monotonous, plexiform structure of tumour
-
DFSP formed both by fibroblastic and histiocytic elements
-
Hemosiderin deposits beneath the tumour
-
Immunostain positive for CD34
| Skin cancer of the dermis | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Chromosome abnormalities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit]
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
|