East Germany: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Former country in Central Europe}} | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
[[File:Europe-GDR_(orthographic_projection).svg|thumb|right|East Germany in Europe]] | |||
'''East Germany''', officially known as the '''German Democratic Republic''' ('''GDR'''), was a country that existed from 1949 to 1990 in the eastern part of what is now Germany. It was established in the Soviet-occupied zone of post-World War II Germany and was a member of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. | |||
East Germany was a | |||
== | ==History== | ||
== | ===Formation=== | ||
[[File:Soviet_Sector_Germany.png|thumb|left|Soviet sector of Germany]] | |||
East Germany was formed on October 7, 1949, following the division of Germany into occupation zones by the Allied powers after World War II. The Soviet Union controlled the eastern zone, which became the GDR, while the western zones, controlled by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France, became the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany). | |||
== | ===Political Structure=== | ||
[[File:Bundesarchiv_Bild_183-19000-3301,_Berlin,_DDR-Gründung,_Wahl_Pieck,_Grotewohl.jpg|thumb|right|Founding of the GDR]] | |||
The GDR was a socialist state under the leadership of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED). The political system was characterized by a single-party rule, with the SED holding a monopoly on power. The first President of East Germany was Wilhelm Pieck, and the first Prime Minister was Otto Grotewohl. | |||
== | ===Leadership=== | ||
[[File:Opvolger_van_Pieck,_Walter_Ulbricht,_Bestanddeelnr_911-5926_(cropped).jpg|thumb|left|Walter Ulbricht, a key leader of East Germany]] | |||
Walter Ulbricht was a prominent leader in the early years of the GDR, serving as the First Secretary of the SED from 1950 to 1971. He was succeeded by Erich Honecker, who led the country from 1971 until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989. | |||
===Economy=== | |||
East Germany had a centrally planned economy, with state ownership of industry and agriculture. The economy was heavily influenced by Soviet models and was integrated into the Eastern Bloc's economic system, the [[Council for Mutual Economic Assistance]] (Comecon). | |||
===Social and Cultural Life=== | |||
The GDR promoted socialist values and sought to create a distinct East German identity. Education, healthcare, and social services were provided by the state. Cultural life was heavily regulated, with censorship and state control over media and the arts. | |||
==The Berlin Wall== | |||
[[File:West_and_East_Berlin.svg|thumb|right|Map of West and East Berlin]] | |||
One of the most significant symbols of the Cold War was the [[Berlin Wall]], constructed in 1961 to prevent East Germans from fleeing to the West. The Wall divided Berlin into East and West and became a powerful symbol of the division between the communist and capitalist worlds. | |||
==Reunification== | |||
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, marked the beginning of the end for East Germany. Political changes and public pressure led to the opening of the borders and the eventual reunification of Germany on October 3, 1990. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Berlin Wall]] | * [[Berlin Wall]] | ||
* [[Cold War]] | * [[Cold War]] | ||
* [[German reunification]] | * [[German reunification]] | ||
* [[History of Germany]] | |||
[[Category:East Germany]] | |||
[[Category:Former countries in Europe]] | [[Category:Former countries in Europe]] | ||
[[Category:States and territories established in 1949]] | [[Category:States and territories established in 1949]] | ||
[[Category:States and territories disestablished in 1990]] | [[Category:States and territories disestablished in 1990]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:56, 23 March 2025
Former country in Central Europe

East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country that existed from 1949 to 1990 in the eastern part of what is now Germany. It was established in the Soviet-occupied zone of post-World War II Germany and was a member of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War.
History[edit]
Formation[edit]

East Germany was formed on October 7, 1949, following the division of Germany into occupation zones by the Allied powers after World War II. The Soviet Union controlled the eastern zone, which became the GDR, while the western zones, controlled by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France, became the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany).
Political Structure[edit]

The GDR was a socialist state under the leadership of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED). The political system was characterized by a single-party rule, with the SED holding a monopoly on power. The first President of East Germany was Wilhelm Pieck, and the first Prime Minister was Otto Grotewohl.
Leadership[edit]

Walter Ulbricht was a prominent leader in the early years of the GDR, serving as the First Secretary of the SED from 1950 to 1971. He was succeeded by Erich Honecker, who led the country from 1971 until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989.
Economy[edit]
East Germany had a centrally planned economy, with state ownership of industry and agriculture. The economy was heavily influenced by Soviet models and was integrated into the Eastern Bloc's economic system, the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon).
Social and Cultural Life[edit]
The GDR promoted socialist values and sought to create a distinct East German identity. Education, healthcare, and social services were provided by the state. Cultural life was heavily regulated, with censorship and state control over media and the arts.
The Berlin Wall[edit]
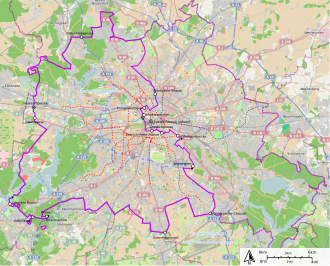
One of the most significant symbols of the Cold War was the Berlin Wall, constructed in 1961 to prevent East Germans from fleeing to the West. The Wall divided Berlin into East and West and became a powerful symbol of the division between the communist and capitalist worlds.
Reunification[edit]
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, marked the beginning of the end for East Germany. Political changes and public pressure led to the opening of the borders and the eventual reunification of Germany on October 3, 1990.