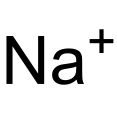Sodium chlorite: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Category:Water treatment]] | [[Category:Water treatment]] | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
== Sodium_chlorite == | == Sodium_chlorite == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:58, 17 March 2025
Sodium chlorite is a chemical compound used in a variety of applications, including water purification, bleaching, and manufacturing. It is a white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. Sodium chlorite is often used in the production of chlorine dioxide, a powerful oxidizing agent.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is an inorganic salt that is produced by the reaction of chlorine dioxide with sodium hydroxide. It is a strong oxidizer and can react violently with organic materials, leading to fire or explosion. Sodium chlorite is stable under normal conditions, but it decomposes to form oxygen and sodium chloride when heated.
Uses[edit]
Sodium chlorite is used in a variety of applications due to its strong oxidizing properties. It is used in water treatment plants to kill bacteria and other microorganisms. In the paper industry, it is used as a bleaching agent. Sodium chlorite is also used in the production of disinfectants and antiseptics.
Health Effects[edit]
Exposure to sodium chlorite can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Ingestion can lead to nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Long-term exposure can lead to more serious health effects, including damage to the red blood cells.
Regulation[edit]
In many countries, the use of sodium chlorite is regulated due to its potential health effects. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates the use of sodium chlorite in drinking water.
See Also[edit]
Sodium_chlorite[edit]
-
Sodium ion
-
Chloride ion
-
Sodium 3D model
-
Chlorite 3D van der Waals model
-
Sodium chlorite 450g