N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Biochemistry]] | [[Category:Biochemistry]] | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
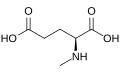
File:N-methyl-L-glutamic acid.svg|N-methyl-L-glutamic acid | File:N-methyl-L-glutamic acid.svg|N-methyl-L-glutamic acid | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:46, 17 March 2025
N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid is an amino acid derivative that is structurally related to the common amino acid L-glutamic acid. Unlike L-glutamic acid, which plays a pivotal role in cellular metabolism and neurotransmission, N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid has a methyl group attached to its nitrogen atom, altering its properties and functions.
Structure and Properties[edit]
N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid shares the same backbone as L-glutamic acid, with the primary difference being the addition of a methyl group (-CH3) to the nitrogen atom in the amino group. This modification significantly impacts the molecule's behavior in biological systems. The presence of the methyl group makes N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid a non-proteinogenic amino acid, meaning it is not directly coded for by DNA in ribosomal protein synthesis.
The chemical formula of N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid is C6H11NO5, and it possesses one carboxyl group (-COOH) and one amino group (-NH-CH3), similar to other amino acids, but with the unique characteristic of methylation at the nitrogen atom.
Biological Significance[edit]
N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid is not as widely studied as L-glutamic acid, which is known for its role as a neurotransmitter and a precursor to the synthesis of proteins. However, the methylation of amino acids, including glutamic acid, can affect neurotransmission and has been implicated in various biological processes, including epigenetic regulation of gene expression.
Methylated amino acids like N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid can arise through post-translational modifications of proteins or can be synthesized de novo in cells. The specific functions and pathways involving N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid are areas of ongoing research, with potential implications in neuroscience, metabolism, and disease.
Potential Applications and Research[edit]
Research into N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid and other methylated amino acids is an active area of interest, particularly in the context of neurobiology and disease. Methylation processes are crucial in the brain's development and function, and abnormalities in these processes have been linked to various neurological disorders.
Understanding the role of N-Methyl-L-glutamic acid could lead to insights into the mechanisms of neurotransmission, neurodevelopmental disorders, and the potential therapeutic targeting of methylation pathways in disease. Additionally, studying the metabolism and function of methylated amino acids can contribute to our understanding of epigenetic regulation and the complex interplay between genetics, metabolism, and disease.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
-
N-methyl-L-glutamic acid