Leptosidin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Leptosidin.svg|Leptosidin | File:Leptosidin.svg|Leptosidin | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:34, 17 March 2025
Leptosidin is a bioactive compound found in the Leptospermum scoparium plant, commonly known as the Manuka tree. It is known for its potential antimicrobial properties and is a subject of ongoing research in the field of natural medicine and pharmacology.
History[edit]
The discovery of Leptosidin can be traced back to the extensive research on the Manuka tree, a plant native to New Zealand and southeast Australia. The Manuka tree has been used in traditional Maori medicine for centuries, and modern science has begun to explore the potential health benefits of its components, including Leptosidin.
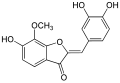
Chemical Structure[edit]
Leptosidin is a phenolic compound, a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The exact chemical structure and properties of Leptosidin are still under investigation.
Potential Health Benefits[edit]
Research into Leptosidin has suggested potential health benefits, particularly in relation to its antimicrobial properties. Studies have indicated that Leptosidin may be effective against a range of bacteria, including those resistant to traditional antibiotics. However, further research is needed to fully understand the potential of this compound in medical applications.
Future Research[edit]
The potential of Leptosidin as a natural antimicrobial agent has sparked interest in the scientific community. Future research will likely focus on understanding its exact mechanism of action, potential side effects, and the feasibility of its use in clinical settings.
See Also[edit]
-
Leptosidin