Lawsone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
==Lawsone== | ==Lawsone== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:33, 17 March 2025
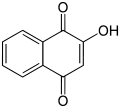
Lawsone (also known as hennotannic acid or natural orange 6) is a red-orange dye that is obtained from the henna plant (Lawsonia inermis). It is a hydroxy naphthoquinone, a type of compound with a structure that includes a naphthalene ring with two ketone substituents. It is primarily used as a staining agent in cosmetics and tattoos, particularly in mehndi, the traditional art of henna tattooing.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit]
Lawsone's chemical formula is C10H6O3. It is a crystalline solid that is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. Its molecular weight is 174.15 g/mol. The compound has a melting point of 192°C and a boiling point of 390°C.
Uses[edit]
Lawsone is primarily used as a dye. When applied to the skin, it reacts with the proteins in the skin to produce a dark stain. This property makes it popular for use in cosmetics and tattoos. It is also used in hair dyes, where it can produce a range of colors from red to brown.
In addition to its use as a dye, lawsone has also been studied for its potential medicinal properties. Some research suggests that it may have antimicrobial and antifungal effects, although more research is needed in this area.
Safety[edit]
While lawsone is generally considered safe for topical use, it can cause allergic reactions in some people. It is also toxic if ingested, and can cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It is not recommended for use on broken or irritated skin.
See Also[edit]
Lawsone[edit]
-
HNQ structure
-
Lawsone 3D ball model