Hyperprolinemia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:L-proline-skeletal.png|Hyperprolinemia | File:L-proline-skeletal.png|Hyperprolinemia | ||
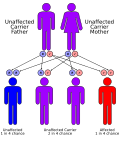
File:autorecessive.svg|Hyperprolinemia | File:autorecessive.svg|Hyperprolinemia | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 00:02, 17 March 2025
Hyperprolinemia is a condition characterized by elevated levels of a particular amino acid called proline in the blood. This condition can occur in two forms, known as type I and type II.
Type I Hyperprolinemia
Type I hyperprolinemia is the milder form of the condition. It is often detected during newborn screening or during family studies following the diagnosis of a sibling. Most individuals with type I hyperprolinemia are asymptomatic and have normal growth and development.
Type II Hyperprolinemia
Type II hyperprolinemia is a more severe form of the condition. It is associated with intellectual disability and seizures.
Causes
Hyperprolinemia is caused by mutations in the PRODH gene (type I) or the ALDH4A1 gene (type II). These genes provide instructions for making enzymes that are involved in the breakdown of the amino acid proline.
Diagnosis
Hyperprolinemia is diagnosed based on the symptoms, clinical exam, and confirmed by laboratory testing showing elevated levels of proline in the blood.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for hyperprolinemia. Management is supportive and depends on the symptoms in each individual.
See Also
References
- Genetics Home Reference. Hyperprolinemia. Available at: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/hyperprolinemia
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Hyperprolinemia Type I. Available at: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/hyperprolinemia-type-i/