Glyclopyramide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
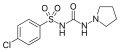
File:Glyclopyramide.svg|Glyclopyramide | File:Glyclopyramide.svg|Glyclopyramide | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:33, 16 March 2025
Glyclopyramide is a sulfonylurea compound that is used as an antidiabetic agent. It is classified under the second generation of sulfonylureas and is used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Glyclopyramide works by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas. It binds to the sulfonylurea receptor in the pancreatic beta cells, leading to an influx of calcium ions. This triggers the release of insulin, which helps to lower blood glucose levels.
Side Effects[edit]
Like other sulfonylureas, Glyclopyramide can cause hypoglycemia as a side effect. Other potential side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. It is important to monitor blood glucose levels regularly while taking this medication.
Contraindications[edit]
Glyclopyramide is contraindicated in patients with type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. It should also not be used in patients with a known hypersensitivity to sulfonylureas.
Interactions[edit]
Glyclopyramide may interact with other medications, including beta blockers, diuretics, and steroids. These interactions can affect the effectiveness of the medication and may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.