Cannabivarin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[Category:Pharmacology]] | [[Category:Pharmacology]] | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Cannabivarin.svg|Cannabivarin.svg | File:Cannabivarin.svg|Cannabivarin.svg | ||
File:Cannabivarin_molecule_ball.png|Cannabivarin_molecule_ball.png | File:Cannabivarin_molecule_ball.png|Cannabivarin_molecule_ball.png | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:31, 16 March 2025
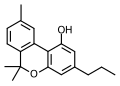
Cannabivarin (CBV) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the Cannabis plant. It is one of several compounds found in Cannabis, along with THC, CBD, and others. CBV is an analog of CBN, with the side-chain shortened by two methylene bridges.
Chemistry[edit]
Cannabivarin is a homolog of CBD, with the side-chain shortened by two methylene bridges (CH2 groups). Despite the structural similarity, the effects of CBV are significantly different from those of CBD. The exact reason for this difference in activity is currently unknown.
Pharmacology[edit]
The pharmacology of Cannabivarin is not well understood. It is known to have no psychoactive effects, unlike THC. However, it has been found to have some potential therapeutic effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-convulsant, and neuroprotective effects.
Potential Therapeutic Uses[edit]
Research into the potential therapeutic uses of Cannabivarin is still in its early stages. However, preliminary studies suggest that it may have potential in the treatment of epilepsy, due to its anti-convulsant effects. It may also have potential in the treatment of inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases, due to its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of Cannabivarin varies by country. In some countries, it is classified as a controlled substance, while in others it is legal to use for medical purposes.
See Also[edit]
-
Cannabivarin.svg
-
Cannabivarin_molecule_ball.png