Bromine trifluoride: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category:Fluorine compounds]] | [[Category:Fluorine compounds]] | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
== Bromine trifluoride gallery == | == Bromine trifluoride gallery == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:12, 16 March 2025

Bromine trifluoride (BrF3) is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula BrF3. It is a chemical compound consisting of bromine and fluorine, where bromine has a oxidation state of +3. This compound is known for its aggressive reactivity and its ability to react with most organic compounds, including hydrocarbons, at room temperature.
Properties[edit]
Bromine trifluoride is a colorless, fuming liquid at room temperature with a pungent odor. It is highly reactive, corrosive, and can release toxic fumes of bromine and fluorine gases upon contact with moisture or water. BrF3 has a boiling point of 125.8°C and a melting point of 8.77°C. It is soluble in sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), but reacts violently with water and organic materials.
Production[edit]
Bromine trifluoride is produced industrially by the direct reaction of elemental bromine (Br2) with fluorine gas (F2) at temperatures of 20-130°C. The reaction is highly exothermic and requires careful control to prevent explosions.
Applications[edit]
Due to its strong oxidizing and fluorinating properties, BrF3 is used in a variety of applications. It is employed in the production of uranium hexafluoride (UF6) in the processing of nuclear fuel, as a fluorinating agent in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of certain fluorocarbons. Additionally, it has been used as a rocket propellant oxidizer and in the etching of silicon in the semiconductor industry.
Safety[edit]
Handling of bromine trifluoride requires strict safety precautions due to its extreme reactivity and corrosiveness. It can cause severe burns upon contact with skin and is highly damaging to the eyes, respiratory system, and mucous membranes. Appropriate protective equipment, including respirators, gloves, and eye protection, must be worn when working with this compound. Storage areas should be well-ventilated and equipped with materials to neutralize spills.
Chemical Reactions[edit]
BrF3 acts as a strong Lewis acid and can form complexes with a variety of Lewis bases. It readily decomposes in the presence of water to form hydrofluoric acid (HF) and hypobromous acid (HOBr), a reaction that is highly exothermic and can be explosive under certain conditions.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Due to its high reactivity and potential to release toxic gases, the environmental impact of bromine trifluoride must be carefully managed. Releases into the environment should be avoided, and any spills must be contained and neutralized promptly.
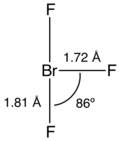
Bromine trifluoride gallery[edit]
-
BrF3 Structure
-
Bromine trifluoride 3D vdW